An Earned Value Management Software: Primavera P6
There are many tools, techniques, and software tools that exist in the field of project management to improve the planning and monitoring capabilities of project teams. Earned Value Management EVM system is one of the most widely used ones which helps to make advanced performance measurements by using formulas. Basically, Earned Value Management EVM is a project management technique used for tracking progress by combining cost and schedule measurements. Planned Value, Actual Cost, and Earned Value are essential elements of this system. Project teams often use Earned Value Management software tools to make performance calculations in complex projects with thousands of activities. Primavera P6 is an advanced Earned Value Management software that enables us to make earned value calculations to analyze the schedule and cost variances of project activities. In this Primavera P6 Tutorial, we will discuss the performance measurement capabilities of Primavera P6 by using an example project.
Table of Contents
How to Monitor the Performance of a Project?
Project managers and stakeholders usually ask these famous questions.
- Are we behind or ahead of schedule?
- Are we over or under budget?
Are the planned and actual figures provide enough information to decide the cost and schedule performance? Actually, making simple planned and actual value calculations do not give proper answers to these questions. Budgeted cost of worked performed” or BCWP is needed to recognize how well the project is performing relative to its original plans.
Simply put, Earned value management is a project control system based on planning, cost control, and performance measurement practices.
Basically, this technique uses three key metrics: planned value, actual cost, and the Earned Value (EV). The below figure illustrates the key metrics of Earned Value.
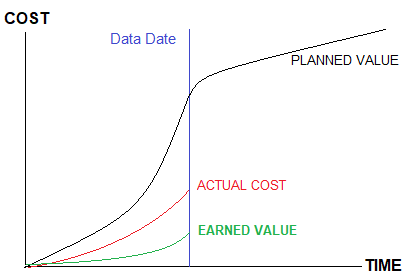
KEY METRICS OF THE EVM
“Planned Value (PV) ” is known as the cost for the work scheduled (BCWS), “Actual Cost (AC)” is the actual cost of the accomplished work. “Earned Value (EV)” is the percent of the total budget completed at a specific point in a given time.
Earned Value Management Formula
Earned Value = % of completed work X Budget at Completion.
https://www.projectcubicle.com/earned-value-management-evm-example/
For better understanding, let’s analyze the sample below.
In a lighting pole project, the total scope of work comprises the erection of 100 lighting poles. As of today 40 of them are erected. Earned Value Management Formula = of completed work X Budget at Completion.
So the progress of work is 40/100 = 40% complete. If the total budgeted cost of this work is $5 M, the Earned Value (EV) is $5 M x 0,4 = $ 2 M.
Primavera P6 Earned Value Management Software
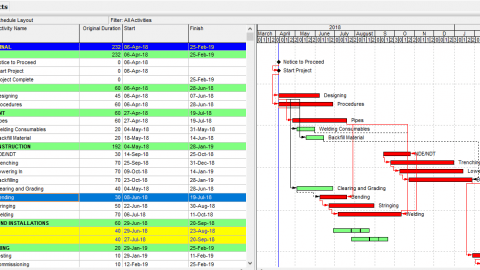
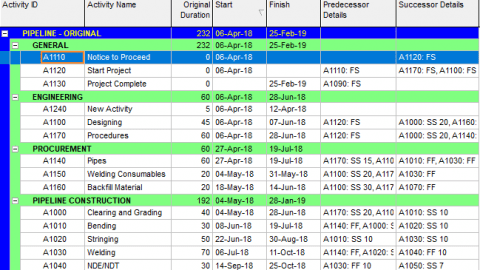
In this article, we will analyze the Primavera P6 Earned Value Management EVM feature by using a sample work schedule. The below figure (Figure 1) displays a pipeline schedule and the baseline.
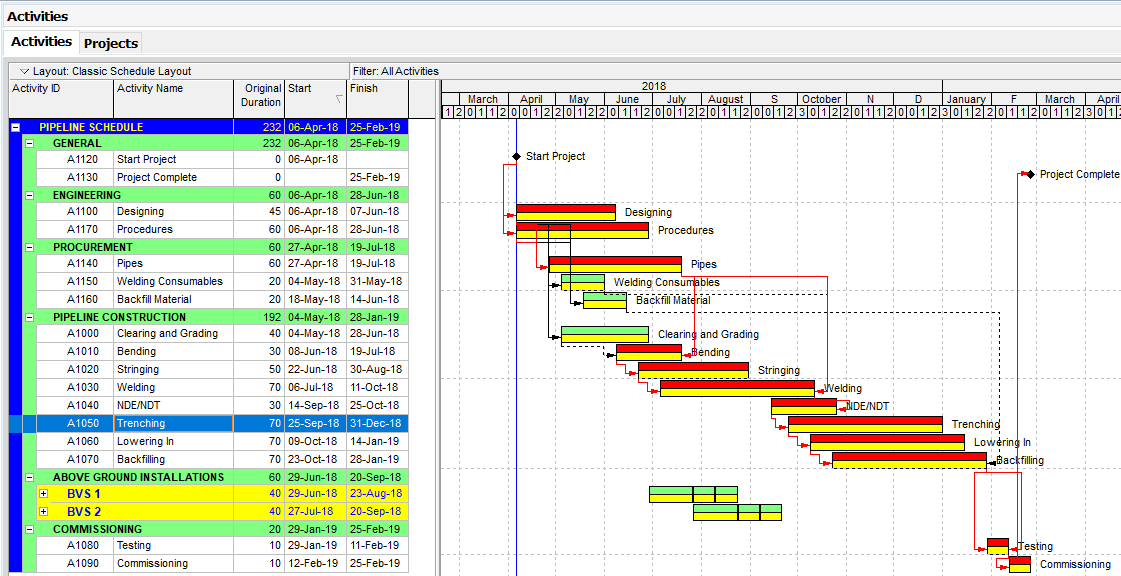
Primavera P6 Earned Value Management EVM – Figure 1 Sample Pipeline Schedule
In this schedule, Welding and NDT activities are listed under Pipeline Schedule WBS. Each welding activity represents 5000 joints in 50 km. In the same way, each NDT (Non-Destructive Testing) activity represents 5000 joints in 50 km. Welding of each joint has a fixed cost of $100 and NDT of each joint has a fixed cost of $30. We assigned non-labor resources to represent the total cost of each activity as shown in Figure 2.
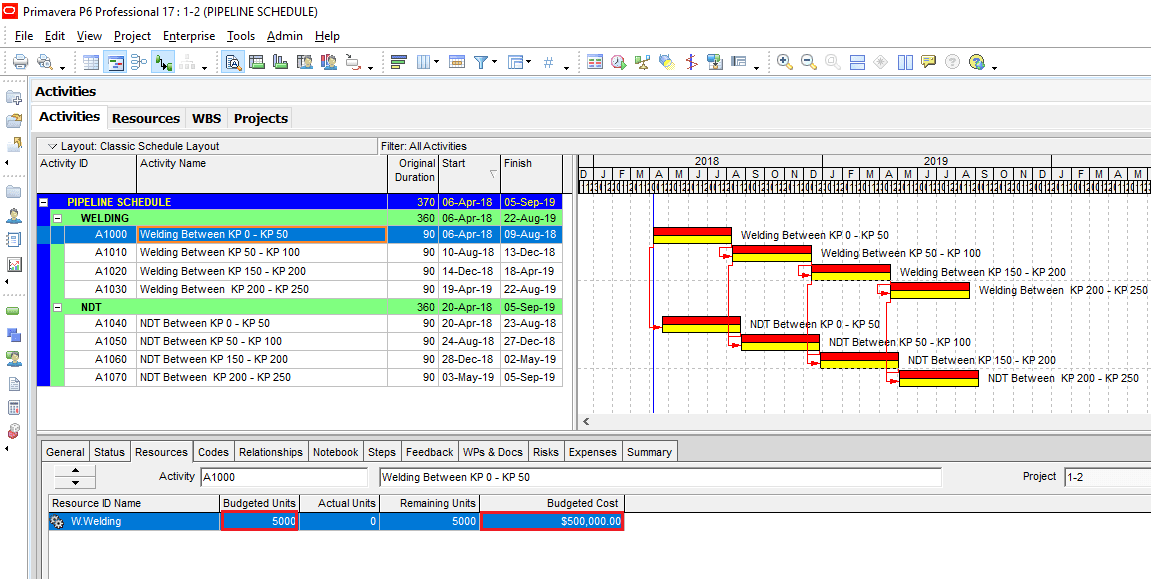
Figure 2 Assigning Resources and Costs
Now we will add the below columns to review the Primavera P6 Earned Value Management EVM calculations as shown in Figure 3.
– Budgeted Total Cost
– Actual Total Cost
– Planned Value Cost
– Earned Value Cost
– Actual Cost
– Schedule Variance
– Schedule Performance Index
– Cost Variance
– Cost Performance Index
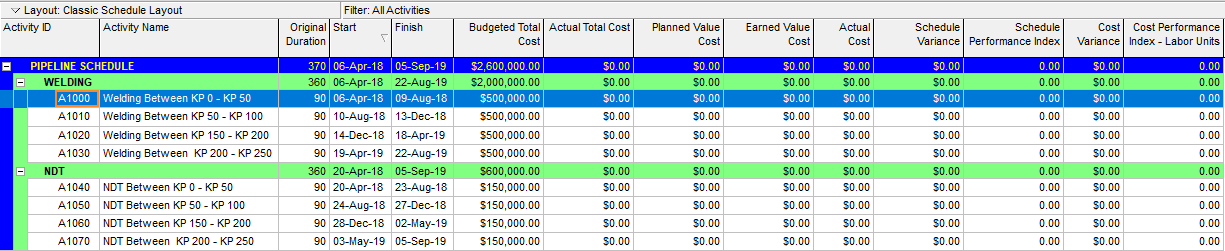
Primavera P6 Earned Value Management EVM – Figure 3 Customizing Columns
We will update the start and finish date of activity A 1000. Let’s assume that the actual start date is 15-Apr-18 and the actual finish date is 30-Aug-18, Figure 4.
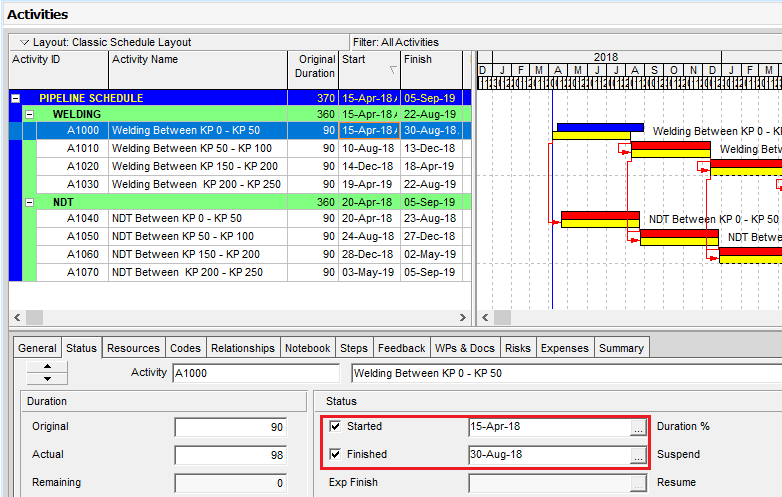
Figure 4 Actual Start and Finish Dates
The actual cost of this activity is $600,000.00. So there is a $100,000.00 cost overrun, Figure 5.
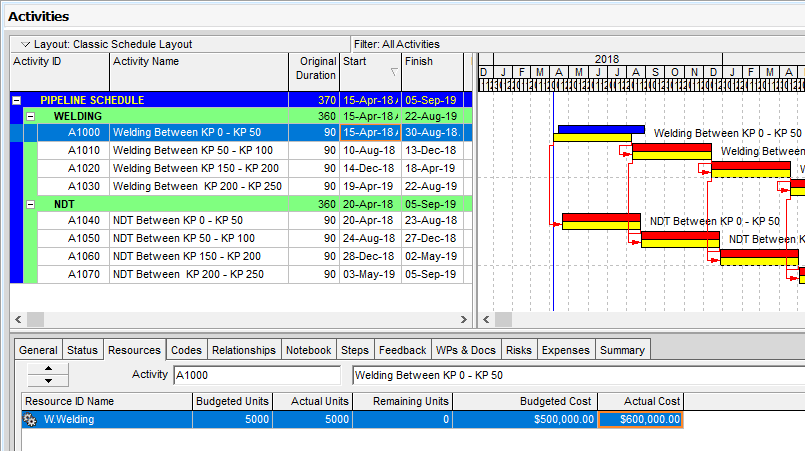
Figure 5 Budgeted Cost, Actual Cost, Cost Overrun
Now we will move the data date to 1-Sep-18 and click the schedule button, Figure 6.
Figure 6 Schedule
As it is seen from Figure 7, Earned Value Management EVM Calculations columns are filled after the update.
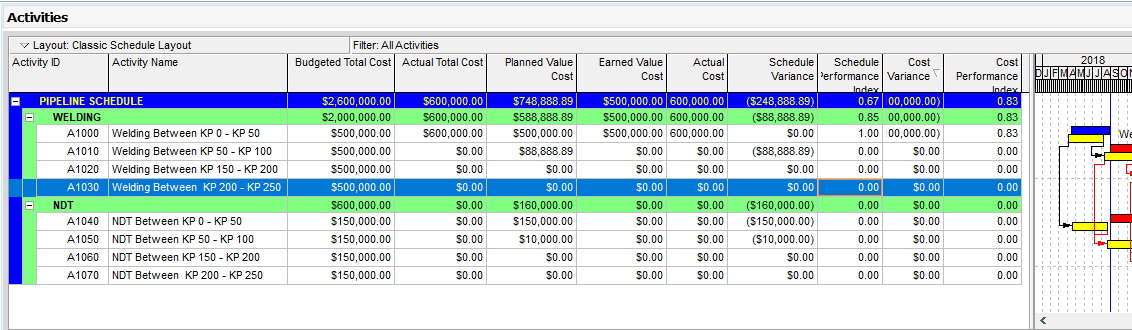
Figure 7 Primavera P6 Schedule Performance Index
Primavera P6 Earned Value Management EVM System
Primavera P6 performed the following earned value calculations for our sample project. Note that the planned value indicates the planned cost between 6-Apr-18 and 01-Sep-18.
Schedule Variance: (Earned Value – Planned Value) = $-248,888.89 Behind the schedule
Cost Variance: (Earned Value – Actual Cost) = $-100,000.00 Over Budget.
Schedule Performance Index : Earned Value / Planned Value = $ 500,000.00 / 748,888.89 = 0.67
Cost Performance Index : Earned Value / Actual Cost = $ 500,000.00 / 600,000.00 = 0.833
Primavera P6 Tutorial for Beginners
Summary
Performance measurement is the process of analyzing the productivity of a project at a specific point. Therefore it should be made periodically to recognize how well the project is going. Without having a proper performance measurement system in place, it will be difficult for a project manager to make decisions.
In this article, we demonstrated the capabilities of Primavera P6 as an Earned Value Management Software. Simply put, Planned Value, Actual Cost and Earned Value are the basic calculations of the earned value management. Schedule Variance and Cost Variance are effective tools for measuring project cost and schedule performance.
In order to perform effective Earned Value Management, WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) of the project should be well organized. Activity relationships should represent real project execution methods and resources which are allocated to the activities should represent the nature of work.
Note that a well-organized project schedule is key to analyze cost and schedule performance variances.
References
Association for Project Management (APM)
See Also
Earned Value Management Example

Irma Gilda is chief executive of Sonic Training and Consultancy Co., the training platform offers project planning and scheduling More than 60 k learners have used the platform to attain professional success. Irma is a professional Primavera P6 Trainer.