Precedence Diagram Method (Activity on Node method)
The Project Management task becomes more challenging considering today’s large and sophisticated projects. Effective time and cost management become more important than before for the success of any kind of project. Therefore project managers and team members use techniques, methods, and tools to plan and manage project schedules. The Precedence Diagram Method (also known as the activity on node method), is a visual presentation technique that is used to create a project network diagram.
Table of Contents
The PDM is used along with the critical path method. Unlike the arrow diagramming method, activities are represented as nodes or boxes and linked by one or more dependencies. The dependencies show the order in which the activities will be performed. In this article, we will talk about common scheduling terms and methods such as the critical path method, arrow diagramming method, and project network diagrams.
Project Network Diagrams
A project network diagram is a visual presentation tool used to demonstrate a project schedule. The PERT Method, Critical Path Method, and Gantt Charts are used along with the project network diagrams. Network diagrams create a framework to demonstrate activities and the activity dependencies from the start to the end date of the project.
Typically, a project network diagram has two main objectives;
- Enables to see the activities and activity dependencies
- Enables to perform critical path calculations.
While creating a work schedule we use two common methods;
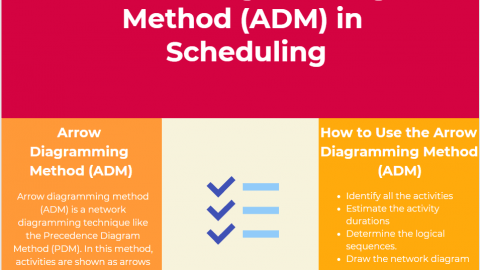
• Arrow Diagramming Method or Activity on Arrow Method (ADM)
• Precedence Diagram Method or Activity on Node Method (PDM)
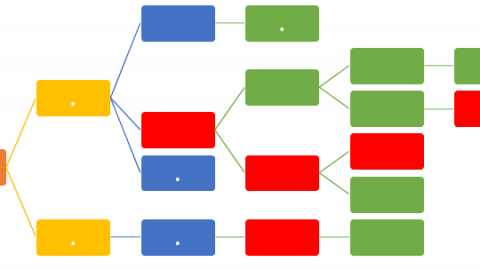
The arrow diagram shows the activities as arrows. The relationships between the activities are represented by nodes. Since the activities are represented as arrows, the length of the arrow shows the activity duration. The precedence diagram method, on the other hand, shows the activities as nodes.
Now, let’s go deeper into the precedence diagram method.
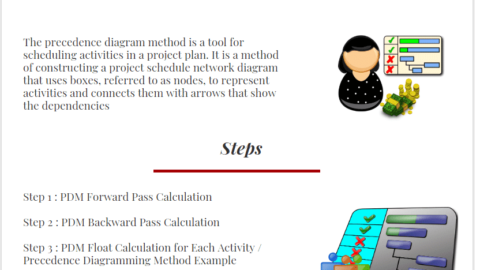
What is the Precedence Diagram Method (Activity on Node Method)?
In Precedence Diagram Method (PDM), nodes or boxes are used to represent activities and arrows show the relationships. While creating a schedule by using this method, the activity dependencies must be determined. During this determination process, Predecessor and Successor activities must be specified.
Predecessor Activity: A predecessor activity is an activity whose start or finish controls the start or finish of another activity
Successor Activity: A successor activity is an activity whose start or finish is controlled by the start or finish of another activity
Dependencies in the Precedence Diagram Method (PDM)
There are four types of relationships in the Precedence Diagram Method between the activities.
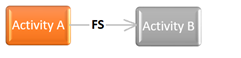
Finish to Start: A successor activity cannot start until a predecessor activity has finished
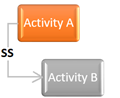
Start to Start: A successor activity cannot start until a predecessor activity has started
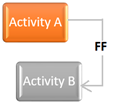
Finish to Finish: A successor activity cannot finish until a predecessor activity has finished
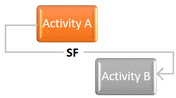
Start to Finish: A successor activity cannot finish until a predecessor activity has started
In the arrow diagramming method, only one type of relationship(FS) can be used. Actually, just one type of relationship can not represent the real work to be performed all the time. Therefore, using four types of relationships provide clarity regarding the dependencies.
Finish to Start is the most common dependency in project network diagrams. Depending on the type of dependency a lead or lag may be used to represent the nature of activity relationships.
Lead is the time that an activity precedes the start or finish of its successor.
Lag is the time that an activity is delayed from the start or finish of its predecessor.
What are the Differences Between the Precedence Diagram Method and the Arrow Diagram Method?
Here below are the main differences between the arrow diagramming method and the precedence diagramming method.
- For types of relationships (FS, SS, SF, FF) can be used in the precedence diagram method. However, in the arrow diagram method, you can use only the FS (finish to start) relationship.
- Activities are represented as arrows in the arrow diagraming method. On the other hand, activities are represented as boxes or nodes in the precedence diagram method.
- The length of an arrow represents the duration of an activity in the arrow diagram method. However, the length of an arrow shows nothing in the precedence diagram method.
- A dummy activity is used to implement a specific relationship between two activities in the arrow diagramming method. On the other hand, there is no dummy activity in the precedence diagramming method.
Summary
Project planning is an important task for the successful completion of a project. Estimating activity durations, deciding activity relationships, calculating the total float, and analyzing the critical path of the schedule are some of the critical efforts of project planning and scheduling.
Network scheduling techniques are used in order to determine the project’s critical path and identify the relocation of resources to meet the project time management requirements.
With the help of software, it is very easy to create the schedule network diagrams and analyze the critical path in the right way. Also, using network diagramming software such as Primavera P6 or Microsoft Project Professional enables project managers, planning engineers, and schedulers to make updates and detailed analyzes quickly. In this article, we discussed some of the important scheduling concepts and listed the main differences between the Precedence Diagram Method and the Arrow Diagram Method.
External Reference
See Also
Precedence Diagramming Method Example
Arrow Diagramming Method Example

Irma Gilda is chief executive of Sonic Training and Consultancy Co., the training platform offers project planning and scheduling More than 60 k learners have used the platform to attain professional success. Irma is a professional Primavera P6 Trainer.