BIM vs CAD: Exploring the Differences and Benefits
Introduction
In the world of design and construction, two key technologies have revolutionized the way professionals approach their work: Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Computer-Aided Design (CAD). While both BIM and CAD are essential tools for architects, engineers, and designers, they have distinct differences and offer unique benefits. In this article, we will delve into the comparison of BIM vs CAD, exploring their features, applications, and advantages.
Table of Contents
BIM vs CAD: What Sets Them Apart?
BIM: The Future of Building Design and Construction
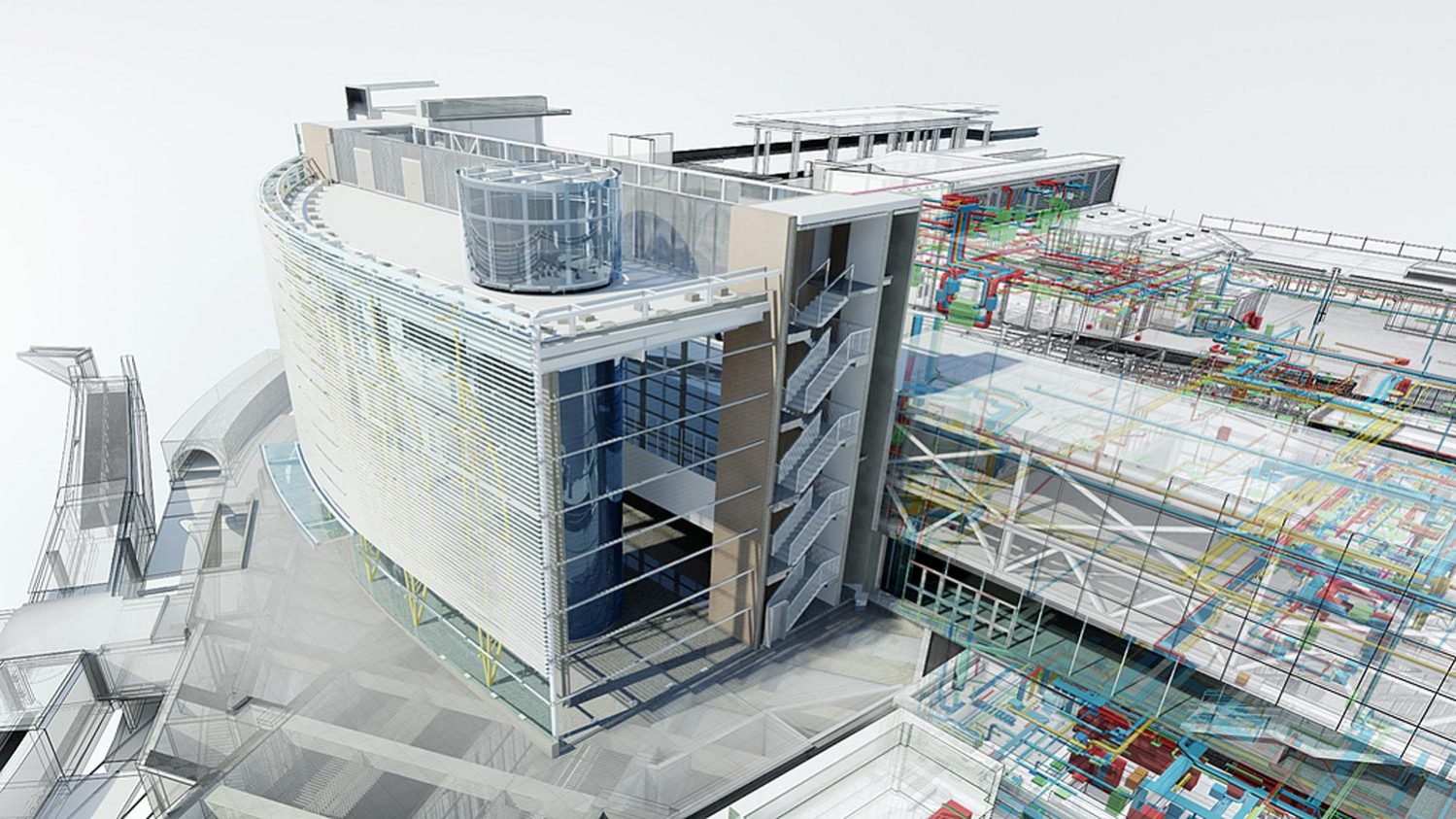
Building Information Modeling, commonly known as BIM, is a sophisticated technology that allows professionals to create, manage, and optimize digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of buildings. Also, BIM goes beyond the capabilities of CAD by providing an integrated approach that incorporates data-rich 3D models, parametric elements, and comprehensive information about the building’s lifecycle.
BIM Applications in Architecture and Engineering
Revit or BIM has become an indispensable tool in architecture and engineering. Architects leverage BIM to create precise 3D models that aid in visualizing the design and detecting clashes early in the process. Engineers use BIM to simulate complex systems, analyze structural integrity, and streamline the coordination of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems. BIM also facilitates collaboration among professionals, improving communication and reducing errors during construction.
CAD: The Foundation of Digital Design
Computer-Aided Design, commonly referred to as CAD, is a fundamental technology that enables professionals to create accurate 2D and 3D drawings. CAD software provides a range of tools and functionalities to support the design and drafting process, making it an essential tool for architects, engineers, and designers.
CAD Applications in Design and Drafting
AutoCAD or CAD has applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, product design, and manufacturing. Architects use CAD to produce detailed floor plans, elevations, and sections, enabling precise visualization of the proposed structure. Engineers rely on CAD to create technical drawings, design components, and analyze structural integrity. CAD also plays a vital role in industrial design and mechanical engineering, facilitating the development of complex products and machinery.
BIM vs CAD: A Detailed Comparison
Now that we have a brief understanding of BIM and CAD let’s delve into a detailed comparison of their key features and benefits.
1. Data Integration and Collaboration
BIM: BIM is renowned for its ability to integrate vast amounts of data into a central model. This data integration promotes collaboration among project stakeholders, allowing seamless information exchange and real-time updates.
CAD: CAD software typically focuses on design creation rather than data integration. While it allows collaboration through file sharing, it lacks the extensive data integration capabilities offered by BIM.
2. Visualization and 3D Modeling
BIM: BIM offers advanced 3D modeling capabilities, allowing professionals to create highly detailed and accurate representations of buildings. This enables stakeholders to visualize the project in a realistic manner, facilitating better decision-making.
CAD: CAD software provides 3D modeling features but is primarily known for its 2D drafting capabilities. While it allows the creation of 3D models, they may lack the level of detail and realism offered by BIM.
3. Parametric Design and Analysis
BIM: One of the significant advantages of BIM is its ability to create parametric elements. These elements possess intelligent properties that allow them to respond dynamically to changes. BIM also facilitates in-depth analysis of various aspects, such as structural integrity, energy efficiency, and cost estimation.
CAD: While CAD allows the creation of intelligent objects, it may not offer the same level of parametric control and analysis as BIM. CAD software is primarily focused on design creation and drafting rather than comprehensive analysis.
4. Lifecycle Management and Facility Maintenance
BIM: BIM shines in the realm of lifecycle management and facility maintenance. By incorporating comprehensive data about building components and systems, BIM enables efficient facility management throughout its lifecycle. This includes tasks such as maintenance planning, asset management, and renovation or retrofitting projects.
CAD: CAD software is not typically equipped with robust lifecycle management capabilities. It is primarily used for design creation and may not provide the necessary functionalities for facility maintenance and management.
BIM vs CAD in Construction: What Sets Them Apart?
Understanding BIM (Building Information Modeling)
BIM is an advanced digital tool that allows construction professionals to create and manage a 3D model of a building or infrastructure project. It goes beyond traditional 2D representations and incorporates valuable information such as geometry, spatial relationships, properties, quantities, and more. BIM software enables collaboration, information sharing, and visualization throughout the project lifecycle, from conceptualization to maintenance.
Exploring CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
On the other hand, CAD focuses primarily on creating precise 2D or 3D models of physical objects or structures. It provides detailed representations and technical drawings that aid architects, engineers, and designers in the planning and design phases of a construction project. CAD software is widely used to generate accurate blueprints, floor plans, elevations, and sections, enabling precise measurements and calculations.
Benefits of BIM in Construction
BIM offers several advantages that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and collaboration in the construction industry. Here are some key benefits of using BIM:
- Improved Visualization: BIM creates realistic 3D models that allow stakeholders to visualize the project before construction begins, aiding in better decision-making.
- Enhanced Collaboration: BIM fosters collaboration among various disciplines involved in a project, such as architects, engineers, contractors, and suppliers. This collaborative environment helps streamline workflows and reduce errors.
- Clash Detection: BIM software enables clash detection by analyzing the 3D model for clashes or conflicts between different building elements. Identifying clashes early on minimizes rework and prevents costly on-site issues.
- Efficient Project Management: BIM provides tools for project scheduling, cost estimation, and material tracking. This improves project management by allowing stakeholders to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and optimize resources.
- Sustainable Design: BIM supports sustainability initiatives by analyzing energy consumption, material usage, and environmental impact. It helps architects and engineers make informed decisions to design eco-friendly buildings.

BIM
Advantages of CAD in Construction
While BIM offers a comprehensive approach to construction project management, CAD excels in specific areas. Here are some advantages of CAD:
- Precise Technical Drawings: CAD software specializes in creating accurate and detailed technical drawings, which are essential for architects, engineers, and contractors. These drawings serve as a blueprint for the construction process.
- Efficient Drafting: CAD streamlines the drafting process by automating repetitive tasks. It enables designers to quickly modify designs, incorporate changes, and produce multiple iterations efficiently.
- Ease of Use: CAD software is known for its user-friendly interface and intuitive tools. Designers can easily navigate the software and create complex drawings with precision.
- Industry Standard: CAD has been an industry standard for decades, making it widely recognized and accepted by professionals across the construction sector. Its ubiquity ensures compatibility and interoperability between different stakeholders.
Architecture model house with a blueprint. Vector illustration
BIM vs CAD: Which One to Choose?
The choice between BIM and CAD depends on various factors such as project requirements, team capabilities, and budget. Here are some scenarios where each technology excels:
- Large, Complex Projects: BIM is highly beneficial for large-scale projects with intricate designs and multiple stakeholders. Its ability to integrate information and facilitate collaboration makes it the preferred choice for complex constructions.
- Design Development and Visualization: When the focus is on design development and visual representation, BIM offers a more immersive and interactive experience. It enables clients to understand the project better and provide feedback during the early stages.
- Detailed Technical Drawings: For projects that require precise technical drawings and extensive detailing, CAD remains indispensable. Its specialized tools and accuracy make it the go-to choice for generating intricate construction documentation.
- Cost and Resources: BIM implementation involves a learning curve and initial investment in software and training. For smaller projects with limited budgets and resources, CAD can be a cost-effective alternative without compromising on quality.
BIM vs CAD: Which One Should You Choose?
When it comes to choosing between BIM and CAD, it’s important to consider the specific needs and requirements of your project. BIM offers a holistic and data-driven approach, making it ideal for large-scale projects with complex systems and long-term management needs. On the other hand, CAD excels in precise design creation and drafting tasks, making it valuable for projects that focus on 2D representations.
It’s worth noting that BIM and CAD are not mutually exclusive. In fact, many professionals utilize both technologies in their workflows, leveraging the strengths of each. By integrating CAD files into the BIM environment, you can benefit from the precision of CAD while harnessing the collaborative power and comprehensive information management capabilities of BIM.
Furthermore, the decision between BIM and CAD should also take into account factors such as budget, available resources, and the expertise of your team. While BIM may require a higher initial investment in software, hardware, and training, it offers long-term cost savings through improved coordination, reduced rework, and efficient facility management. CAD, with its accessibility and shorter learning curve, may be a more suitable choice for smaller projects or when 2D drafting tasks are the primary focus.
BIM vs CAD: Driving Innovation and Efficiency
The advent of BIM and CAD has brought about significant advancements in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries. These technologies have streamlined workflows, enhanced collaboration, and empowered professionals to deliver projects with higher precision and accuracy. The benefits of BIM and CAD extend beyond traditional boundaries and have found applications in other industries such as manufacturing, industrial design, and product development.
In addition to their core functionalities, BIM and CAD are constantly evolving, embracing new technologies and methodologies. For example, the integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) into BIM and CAD workflows allows stakeholders to experience designs in immersive environments, improving visualization and decision-making processes. The adoption of cloud-based collaboration platforms has also facilitated real-time information sharing and enhanced remote collaboration capabilities.
As technology continues to advance, the line between BIM and CAD may become even more blurred. We can expect further integration, with CAD software incorporating more data-driven features and BIM software enhancing its design creation and drafting capabilities. This convergence will ultimately empower professionals with comprehensive and flexible tools to meet the evolving demands of the industry.
FAQs about BIM vs CAD
FAQ 1: Is BIM more suitable for large-scale projects?
Answer: BIM’s data integration and collaboration capabilities make it particularly well-suited for large-scale projects. Its ability to manage vast amounts of information and facilitate coordination among stakeholders ensures efficient project execution.
FAQ 2: Can CAD be used alongside BIM?
Answer: Yes, CAD can be used alongside BIM. While BIM provides a comprehensive approach to building design and management, CAD’s 2D drafting capabilities are still valuable for certain tasks. Integrating CAD files into the BIM workflow allows professionals to leverage the strengths of both technologies.
FAQ 3: Which technology is more cost-effective?
Answer: The cost-effectiveness of BIM vs CAD depends on various factors, including the size and complexity of the project, the specific requirements, and the available resources. While BIM may require a higher initial investment, it offers long-term cost savings through improved coordination, reduced rework, and efficient facility management.
FAQ 4: Is there a steep learning curve associated with BIM and CAD?
Answer: Both BIM and CAD software require a learning curve to master. However, CAD software is generally considered more accessible, with a shorter learning curve due to its focus on 2D drafting. BIM’s comprehensive functionalities and data-driven approach may require more time and effort to fully grasp.
FAQ 5: Can BIM and CAD be used in other industries apart from architecture and engineering?
Answer: Yes, BIM and CAD find applications in various industries beyond architecture and engineering. BIM is also utilized in facility management, construction planning, and infrastructure projects. CAD is employed in fields such as industrial design, product development, and manufacturing.
FAQ 6: Are there any disadvantages to using BIM or CAD?
Answer: While BIM and CAD offer numerous benefits, there are some potential disadvantages. BIM may require a higher initial investment in software, hardware, and training. CAD, on the other hand, may have limitations in terms of data integration and collaboration. Additionally, both technologies rely on the availability of skilled professionals to leverage their full potential.
Conclusion
In the evolving world of design and construction, BIM and CAD play vital roles, each offering unique features and benefits. BIM’s data-driven approach, collaboration capabilities, and lifecycle management functionalities make it a powerful tool for architects, engineers, and facility managers. CAD, with its drafting precision and design creation capabilities, remains an essential technology for professionals in various fields. Understanding the differences and strengths of BIM vs CAD enables professionals to make informed decisions and leverage the right tools for their specific projects.
Projectcubicle Recommend
- “Human Resources Dashboard Create in Excel: Streamline Your HR Processes”
- Learn how to create a human resources dashboard in Excel to streamline HR processes.
- “Export Excel into PDF: Simplify Your Data Sharing Process”
- Discover how to export Excel files into PDF format to simplify data sharing.
- “Exponents in Excel: Powering Up Your Formulas”
- A comprehensive guide on using exponents in Excel to enhance your formulas.
- “Exponential Smoothing in Excel: A Comprehensive Guide to Forecasting Techniques”
- Learn about exponential smoothing in Excel and explore forecasting techniques.
Hello, I’m Cansu, a professional dedicated to creating Excel tutorials, specifically catering to the needs of B2B professionals. With a passion for data analysis and a deep understanding of Microsoft Excel, I have built a reputation for providing comprehensive and user-friendly tutorials that empower businesses to harness the full potential of this powerful software.
I have always been fascinated by the intricate world of numbers and the ability of Excel to transform raw data into meaningful insights. Throughout my career, I have honed my data manipulation, visualization, and automation skills, enabling me to streamline complex processes and drive efficiency in various industries.
As a B2B specialist, I recognize the unique challenges that professionals face when managing and analyzing large volumes of data. With this understanding, I create tutorials tailored to businesses’ specific needs, offering practical solutions to enhance productivity, improve decision-making, and optimize workflows.
My tutorials cover various topics, including advanced formulas and functions, data modeling, pivot tables, macros, and data visualization techniques. I strive to explain complex concepts in a clear and accessible manner, ensuring that even those with limited Excel experience can grasp the concepts and apply them effectively in their work.
In addition to my tutorial work, I actively engage with the Excel community through workshops, webinars, and online forums. I believe in the power of knowledge sharing and collaborative learning, and I am committed to helping professionals unlock their full potential by mastering Excel.
With a strong track record of success and a growing community of satisfied learners, I continue to expand my repertoire of Excel tutorials, keeping up with the latest advancements and features in the software. I aim to empower businesses with the skills and tools they need to thrive in today’s data-driven world.
Suppose you are a B2B professional looking to enhance your Excel skills or a business seeking to improve data management practices. In that case, I invite you to join me on this journey of exploration and mastery. Let’s unlock the true potential of Excel together!
https://www.linkedin.com/in/cansuaydinim/