Internet of Things Applications in Industry
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the intelligent interconnection of smart devices via things that can sense and interact with one another. With this technology, a huge number of small-sized, wireless technology-enabled sensor devices can monitor practically all occurrences and collect information in our environment (home, school, workplace, factory, city, etc.). Similarly, the ability to employ data supplied from industrial applications related to production/manufacturing within the information system has revealed another notion known as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Table of Contents
Connecting Things with the Internet
The Internet is growing and evolving. In the early days of the Internet, this progress was slow. Today, the communication capacity and speed of the internet, which is network of networks, has reached extraordinary levels. The huge network system that started in the 1970s. That time, it was enabling very few devices to communicate and forms the basis of the Internet has now enabled more than 50 billion objects to be connect each other. The developing technologies of the Internet allow any device/object to connect to itself. So, the concept of IoT is a new concept that has increased in popularity thanks to the development of modern wireless communication technologies.
Firstly, the basic formation of this concept is the development of applications. And these aim to facilitate human life by enabling the objects in the world to communicate with each other. Therefore, Internet of Things applications are about the ability of objects built on standard communication protocols and capable of communicate via the Internet. People predict that clothes, white goods, furniture, food items, and many electronic devices will be connected to the internet day by day.
Applications of the Internet of Things:
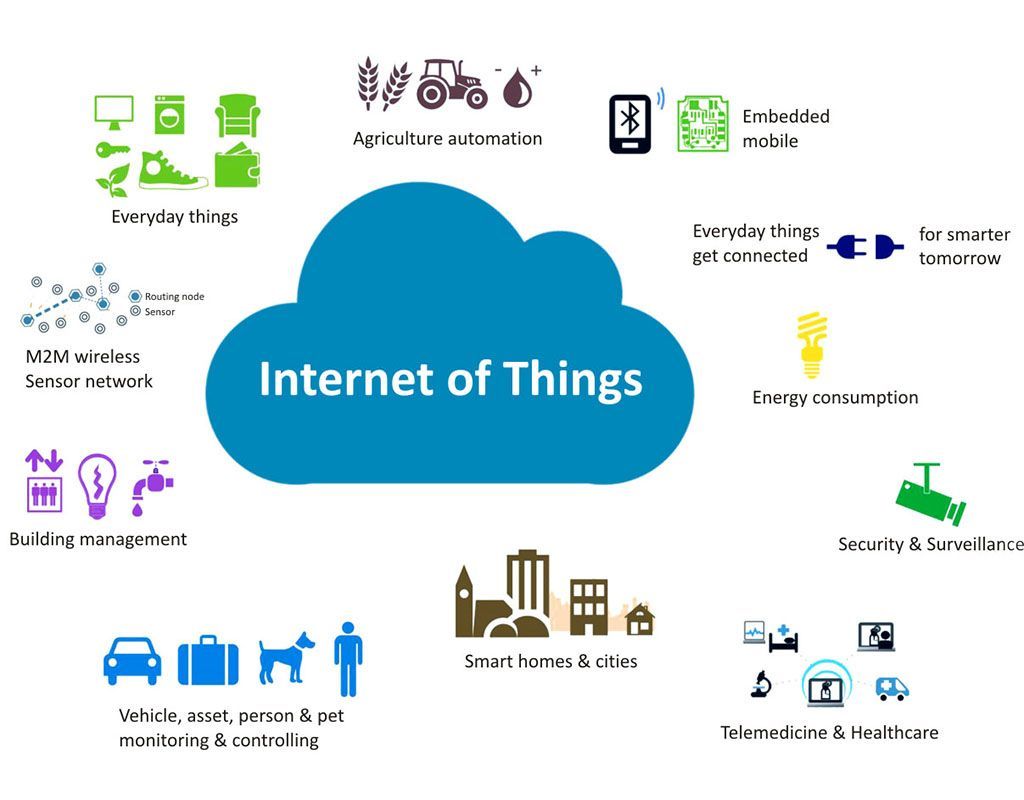
So, Internet of Things applications can work in many areas. Some of these areas are:
- Smart Home Applications,
- Trading Applications.
- Smart City Applications,
- Scientific Work Applications,
- Energy Applications,
- Daily Use Applications,
- Security Applications,
- Manufacturing / Production Applications,
- Construction Applications,
- Public Sector Applications,
- Health Applications,
- Service Provider Applications,
- Agricultural Production,
- Transportation Applications,
Internet of Things Applications in industrial applications:
Rapid developments in IoT have attracted the attention of companies trying to increase production quality and efficiency. Because sensor units, programmable logical control devices (PLC), and relevant systems function in production. And they communicate over wired networks. These systems are controlled from a control center by SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition). Or DCS (Distributed Control Systems) systems and are largely independent of local network systems or the Internet.
There are many important advantages of using IoT together with existing industrial automation systems. Intelligent production machines with IoT capability automatically communicate with each other over the network, controlling production and minimizing operator contribution. Mechanical and electrical failures can be predicted, reducing downtime due to failure. The lack of raw materials for the production of the factory is quickly detected and eliminated. Factory managers can receive real-time information about production and malfunctions from anywhere in the world. Besides, this information can be shared with distribution channels and customers.
Current applications, where we can live an easier life with the Internet of Things, include a wide range of industrial areas, starting from smart homes, cities, factories, and applications in different health and agriculture fields.
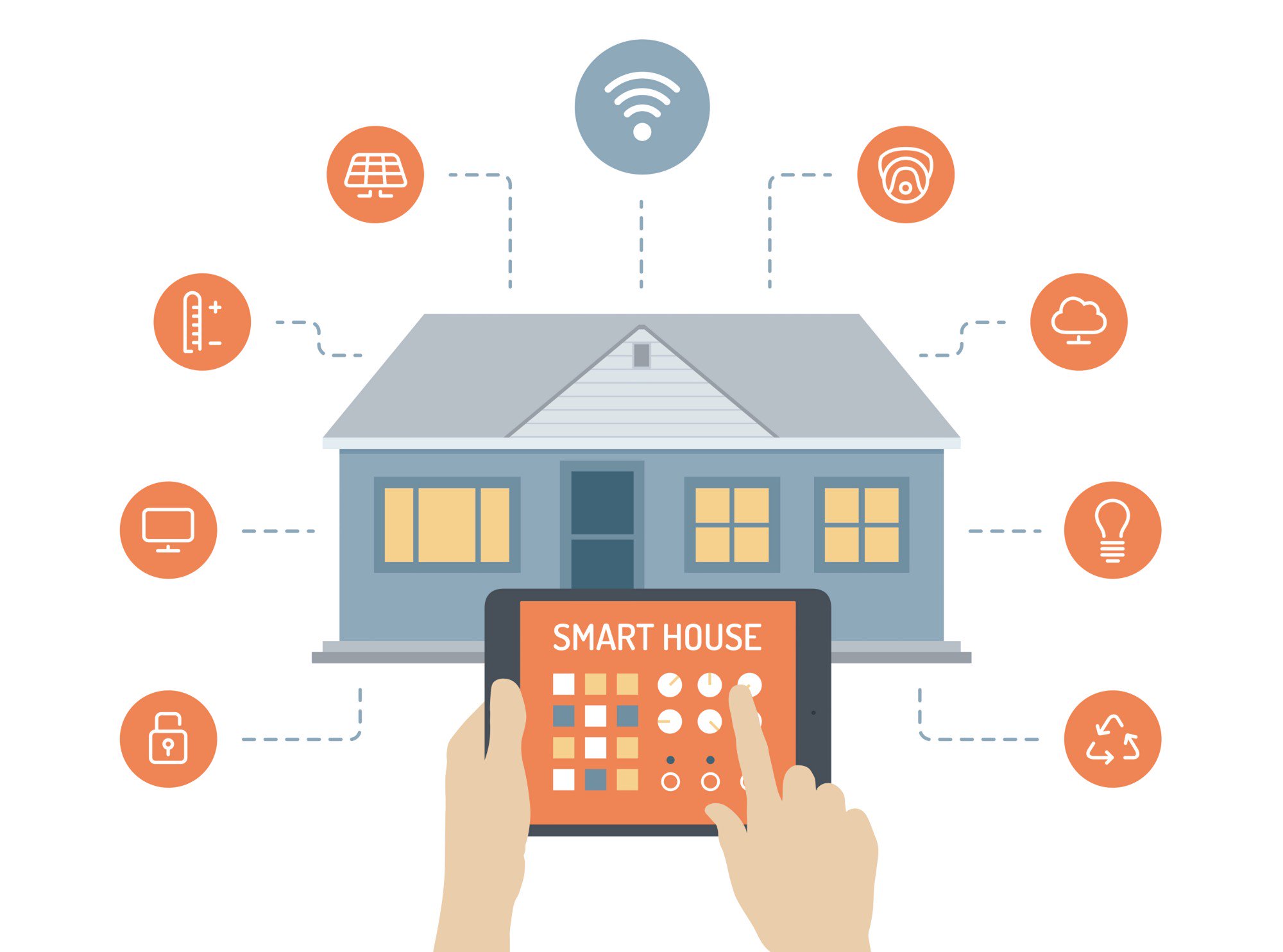
Smart home and factory applications:
It is possible to collect control information about all environmental sensors and devices in the house in a service center on the Internet via a communication medium. And it is possible to analyze this information to increase home security. Also to provide effective energy management or to evaluate it for other purposes. Likewise, operating information from data terminals in production in the factory environment, energy consumption levels, or information from sensors operating with different wireless protocols, such as temperature, humidity, weather conditions, fire alarms, can remotely monitor and control the entire factory with a smartphone application.
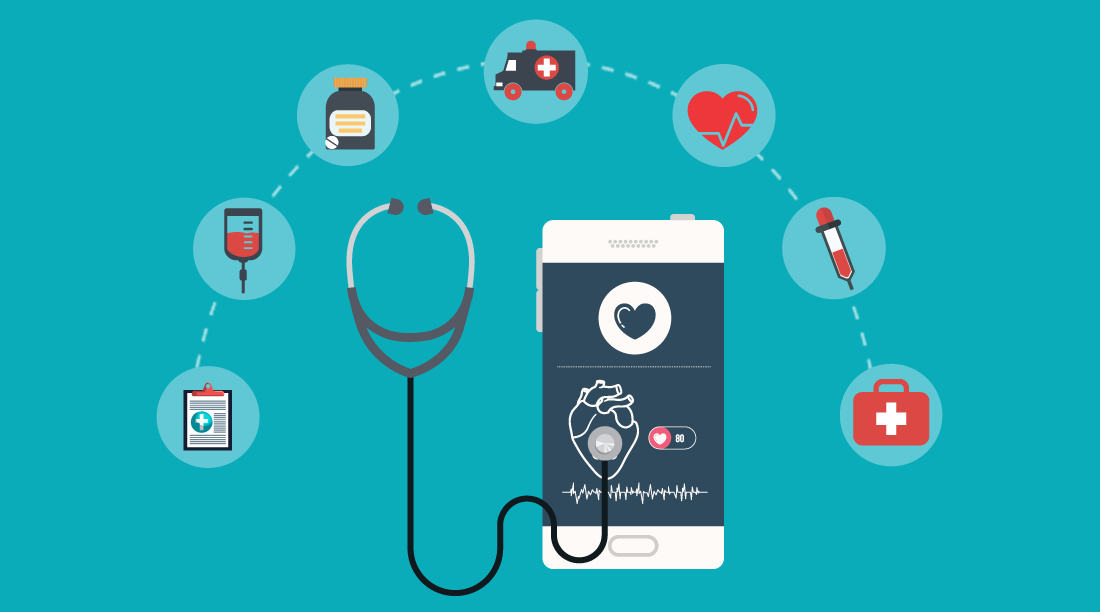
Health applications:
Real-time or periodic health information (blood sugar, blood pressure, heartbeat, body temperature, number of steps, instant physical condition, etc.) of people with chronic diseases or elderly people in need of care are accesible from relevant medical devices. Hence, the ability to monitor and analyze this information by the family and the physician and react immediately in serious situations can only be possible with an Internet of Things applications -based Information System that allows this. Besides, an e-health system that can make studies at different levels in this field more common, ensure interoperability. And it can work together with official health institutions should provide standards in this regard. And dynamically support new applications and protocols that may arise in the future.

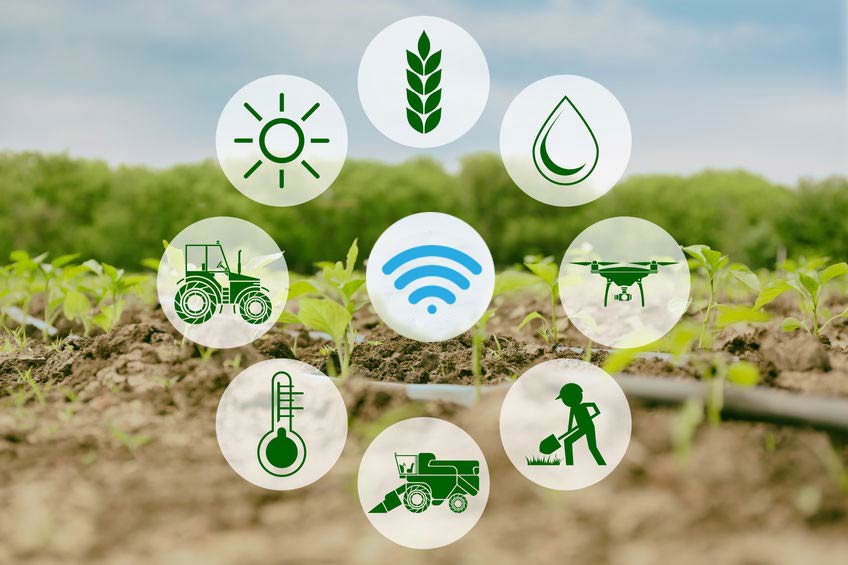
- Agricultural Internet of Things applications: The critical temperature, humidity, and soil values that need to be stable in a greenhouse. And these can be configured and stored on a central computer or the internet after the transmission between the machines. While these machines are part of the IoT system, and can be controlled via mobile users’ phone applications or web access.

Today, IIoT is increasingly prevalent in manufacturing facilities. While the IIoT information flow finds meaning with many applications that facilitate our daily life and business life, it will create many positive effects on issues such as increasing quality in production, reducing costs, energy efficiency, performance, and creating competitive products by combining industry and IoT. However, these positive IIoT features still have some technological and political challenges before they can be fully operational.

Simon Bonghez is currently a Director and Project Management Consultant with LIFESPEED India, and a Project Management Consultant & Speaker.