From Container Security to Spatial Computing, Here Are 5 ‘Obscure’ but Must-Know New Tech for Businesses
Using computers and other technologies has become inevitable for businesses. Most organizations have already digitalized or are in the process of adopting digital technologies. Digital transformation is no longer an option but a must to remain competitive in the modern economy. Many organizations are already familiar with and are using cybersecurity, cloud computing, AI, and various other technologies. They employ AI to automate marketing and customer service. They rely on cloud solutions to ensure safe data storage and high availability of business apps. However, there are still many technologies that business leaders need to know to be up-to-date with technological advancements in businesses and maximize technology’s benefits. Some of the most notable ones related to Container Security to Spatial Computing are described below.
Table of Contents
What is a container security?
What is spatial computing?
Spatial computing is a technology that blends the physical and digital worlds by using advanced sensors, computer vision, and augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR) technologies. It enables computers to understand and interact with the physical environment in real time. Hence, allowing for the seamless integration of digital information and virtual objects into the user’s perception of the physical space. Container Security and spatial computing has applications in various fields. These are including gaming, architecture, healthcare, education, and industrial design.
Infrastructure-as-code
Infrastructure-as-code (IaC) is the management and provisioning of computing infrastructure through code. It entails the writing of machine-readable configuration files to manage an organization’s IT infrastructure instead of the traditional manual process. Infrastructure components such as networks, virtual machines, storage, and services are defined and overseen through code,. They are usually using imperative or declarative configuration languages such as JSON and YAML.
While IaC is mostly used by larger enterprises, its adoption is steadily growing. A Markets and Markets report shows that the IaC market is growing at a CAGR of 24 percent for the forecast period 2022-2027. Organizations are recognizing its benefits although not many, especially smaller businesses, may see an immediate need for it yet.
IaC is a useful technology for IT infrastructure management for a number of important reasons such as container security. For one, it ensures standardization and consistency in applying configurations and resource allocations. It supports infrastructure provisioning automation and efficiency. It also guarantees scalability and flexibility as well as ease in code auditing and version control. These, among many others, are benefits organizations will most likely come to appreciate as they expand and embrace new technologies in running their operations.
Containerization
Related to IaC is the concept of containerization, which is the packaging of applications and their dependencies into containers. Designed to be lightweight and portable, containers encapsulate everything an application requires to run for ontainer security. These include the code, libraries, runtime environment, and settings. Containers operate as isolated environments for applications, separating them from the underlying infrastructure so that they can run consistently and reliably regardless of the environment they are used in.
Containerization is often used in enterprise application deployment and packaging because it simplifies the process and allows developers to build, test, and deploy apps consistently across different environments. It is also used in implementing a microservices architecture, wherein apps are built as small and loosely linked services that can be deployed independently and reiteratively. Additionally, containerization is employed in continuous integration and deployment practices to consistently build, test, and deploy applications throughout the different stages of the software delivery life cycle.
It is important, however, to be mindful of security when using containers. Organizations should properly get acquainted with container security and implement best practices because of the new cyber threats that come with containerization. Misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and software supply chain attacks can undercut the supposed benefits of using containers.
Edge AI and Container Security
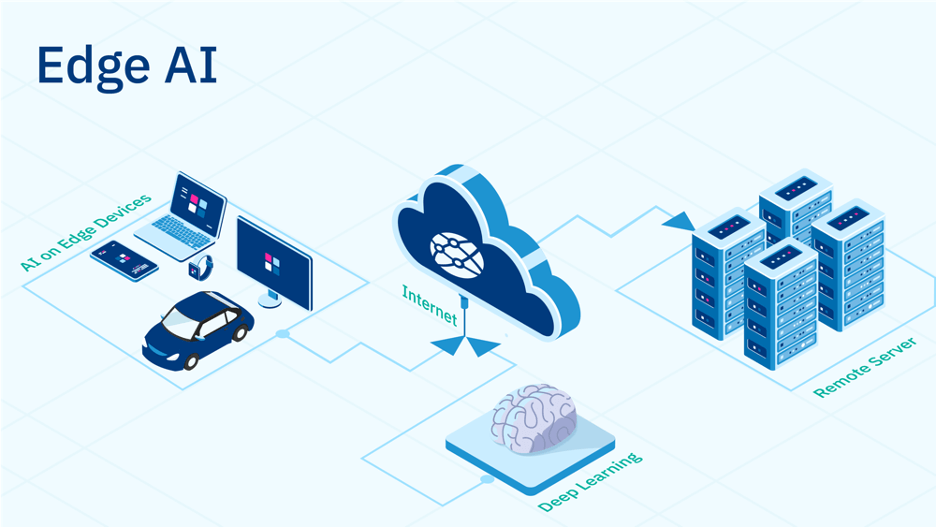
Artificial intelligence is quite a presence across different aspects of business operations nowadays. However, not many are familiar with the concept of edge AI. Also known as edge computing with artificial intelligence, it means the deployment of AI algorithms on edge devices or end-user devices. These include smartphones, IoT devices, cameras, smart appliances, and sensors. With edge AI, the artificial intelligence system resides in the devices and is not centrally located in the cloud like how ChatGPT and other popular AI systems are being operated at present.
Edge AI makes it possible for smart devices to remain functional even without going online. It also results in significantly faster processing because everything happens locally. With data being processed close to the point where data is being generated, data analysis and synthesis take place in real-time, and latency problems become almost nonexistent.
It would be inexpedient if organizations fail to take advantage of this technology, especially if they need to maximize their efficiency and reduce their dependence on the cloud. Additionally, edge AI helps establish greater resilience, as the AI systems will not suffer downtimes or erratic behavior whenever internet connectivity falters or becomes intermittent.
Homomorphic Encryption

Existing encryption technologies are vulnerable to the rise of quantum computers. This sounds foreboding for organizations that seek to maintain the confidentiality and security of their sensitive data. However, homomorphic encryption helps ease this concern by enabling the conversion of data into ciphertext. It is unreadable to non-owners. But the owner of the data can analyze and use it. In other words, encrypted data can work without the need to decrypt it.
Around a month ago, IEEE Spectrum reported the development of chips that can compute with encrypted data. At least six companies are said to be testing the first chips that will enable fully homomorphic encryption (FHE). This may mark the possible obsolescence of the maxim in computer security that everything is hackable. If data is heavily encrypted without necessitating decryption whenever it has to be used, there is essentially no data for cybercriminals to leak, steal, or corrupt.
Businesses can greatly benefit from homomorphic encryption because it removes many of the hurdles associated with existing data encryption technologies. The compulsory encryption-decryption process takes time and material computing overhead, something not many organizations can afford.
Spatial computing and Container Security
Lastly, business leaders should anticipate the future of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies. The recent release of Apple Vision, the iPhone maker’s mixed reality headset system, has sparked renewed interest and fascination over AR, VR, and MR. These technologies may still appear like the butt of jokes at present, but it will not take a long time before they stage a deja vu of what happened when people made fun of large-screen smartphones several years back.
Spatial computing is the use of MR technologies to merge digital content with digital spaces. It enables more immersive interactions and experiences. It allows consumers to do more than ask an AI assistant for information or multimedia content as they do their shopping. Spatial computing makes it possible to do virtual things while also experiencing the real world. For businesses, it also provides a wide range of new ways to attract and engage customers.
Developing an Affinity for Technology
There’s more to gain than lose when trying out new technologies. Aversion to technology very rarely benefits organizations, especially in an age when an overwhelming majority of consumers are demonstrating openness to new tech. Business leaders can help their organizations grow further and become more resilient by keeping up with the evolution of technology and becoming familiar with emerging solutions that can help augment business efficiency and competitiveness.

Magdalena Polka is a Business Solution Designer and an Information Technology / Project Management consultant and author with over 15 years of software development, management and project management experience.