Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Explained with Examples
What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)? – In the simplest terms, a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a mark used to screen and measure the performance and efficiency of an activity or a process. There are many key overall performance indicators in most industries, some are almost every day in the business world, such as internet earnings margin. According to the Key Performance Indicators definition, they are used to demonstrate a measurable value in order to express correctly how an organization or project is performing. In this article, we will answer What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)? and discuss the definition and usage of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) examples to provide you a better understanding of the subject.
Table of Contents
What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are a set of general performance metrics that show how accurately a business enterprise achieves its key goals. For that purpose, KPIs should provide a reference point to check whether the strategic and operational improvements are in place for organizations. Also, they should be helpful to examine the successes of similar organizations to make a comparison.
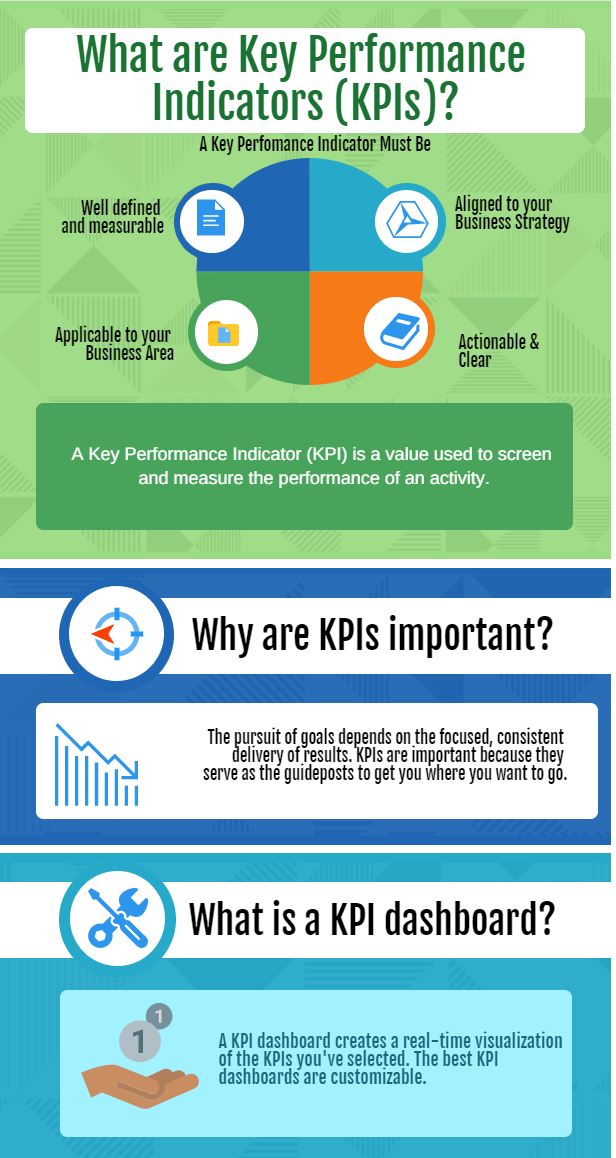
Basically, a KPI must be:
- Well defined and measurable.
-
Aligned to your Business Strategy
- Applicable to your Business Area (LOB) or department.
Some Examples of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
As discussed above, KPIs are related to an organization’s strategic goals. Therefore, managers use them to check whether they are on target while working towards those goals.
For example;
- A sales team leader can monitor new revenue, overall revenue, new consumer capture to analyze how the sales team performing.
- A user support group will likely measure the number of tickets created by users and review how many of the problems are solved through their support.
- A marketing manager can check the number of sales generated by means of the marketing team of the organization.
- Human resources department measures employee turnover across different relevant criteria.
Managers and key project stakeholders scan these indicators over time and change strategies and practices to develop KPIs to reach the organization’s mid-term and long-term goals.
What are Financial Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)?
Below are some financial Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) metrics examples.
- Profit: This goes aside from saying this, but it’s worth noting anyway because it’s one of the most important overall performance indicators. Remember to analyze both the gross and net profit margin to understand how profitable your company is in generating more returns.
- Cost: Evaluate cost-effectiveness and discover satisfactory methods to minimize and decrease your costs.
- LOB Income Vs. Target: This is a benchmark between your actual and planned income. Scheduling and viewing the differences between these two numbers will help you perceive how your branch is performing.
- Cost of Products Sold: By calculating all production costs for the product your organization sells, you can a higher understanding of what your product unit price should be and your actual profit margin.
These financial KPIs are important in determining how you will sell more than your competitors and generate more revenue.
Leading and Lagging Indicators
Leading and lagging indicators are metrics that evaluate a business’s current conditions (lagging indicator) and predict future conditions (leading indicator). With the help of leading and lagging indicators, organizations can make better projections.
How to Use Lagging Indicators?
Measure overall performance over a past period. Financial metrics are traditional examples. As fashion disclaimer warns, previous overall performance no longer guarantees future returns.
How to Use Leading Indicators?
Includes preparation for future results. For example, the increase in auto parts orders suggests an upward driver in new car production and revenue in the near future.
Outstanding Challenges in Developing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
For most businesses, the goal is to develop and maintain proper and stable KPIs.
- If the organization’s approach and key goals are not clear at this time, warning signs tend to focus solely on monetary results. Over-reliance on monetary indicators leads to an unstable and incomplete view of a business’s health.
- Measures that are considered vital in one environment of the business may no longer be viewed as vital by others.
- If the compensation is tied to the core objectives of the general performance indicators, conflicts of interest are built into the process.
- It can also be difficult to accurately measure and report symptoms or may not be possible if the internal reporting device to guide them is not established.
A serviceable process for uncovering and implementing key general performance indicators consists in the requirement that managers and different contributors often reconsider and revise measures.
Shaping KPIs for Organizational Needs
When deciding which KPIs will provide the most valuable benefits, ask a few questions yourself;
- Are these KPIs derived from an effective strategy?
- Is it easy to understand and implement?
- Are they relevant not only now but also in time?
- Are they no doubt identified?
- Do they fully reflect the organizational process?
- Does it contain elements or parts that the business enterprise can fully manage or influence?
- Do they provide quick feedback?
Proper Use of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
A successfully developed and implemented KPI system includes the usual assessment methods that managers and different stakeholders are exploring which tools of the results. No matter how big an indicator is, it desires to be analyzed and evaluated in order to replicate or even strengthen performance.
*A single KPI range does not describe how a scenario came about or how to develop it. However, a well-defined KPI set can cover numbers that affect where conditions worsen and how they can be improved. Contributing crew members with this knowledge can take action to reinforce the main warning signs and reinforce future high results.
# Quick Tip
A simple method to check if a KPI is being used correctly or is presenting meaningful data is to pass it through the SMART criteria. Each KPI should include:
- Specific goal
- One way to measure goal progress
- Achievable, realistic
- Relevance to the operations
- A sensible time frame for the organization
Summary
In this article, we provide key performance indicators definition and answer What are Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in finance and other disciplines with examples. Note that you need to use Leading and Lagging Indicators if you want to make accurate projections for your business.
See Also
Further Reading

Ananya Prisha is an enterprise level Agile coach working out of Hyderabad (India) and also founder of High Level PM Consultancy. Her goal has been to keep on learning and at the same time give back to the community that has given her so much.








KPI’s are great to measure the performance and make the necessary improvements
With KPI we can follow so many things about our job than we can find problems finally we can solve them , That’s awesome we really need it
Key performance indicators shed light on how well a business is running. KPIs are important to business objectives because they keep objectives at the forefront of decision making. Thank you for sharing. I like it !!!!
KPIs reduce the complexity of many different processes and boil down what is happening into a single number. This can shed light on past developments and future directions. I will share this article with my friend..
KPIs are ubiquitous in modern business.