Decision Tree Analysis Technique and Example
What is the importance of Decision Tree Analysis in project management? Today, we are going to discuss the importance of decision tree analysis in statistics and project management by the help of decision tree example problems and solutions. Effective decision-making process is vital for all organizations. It is the process of making a selection among other alternatives. Mostly uncertain circumstances may affect all the judgments. In the existence of uncertainty, we use the decision tree analysis technique to make the right choices.
Table of Contents
This technique can be used for many different project management cases. For example: Should we upgrade the software that we are using in our organization? Should we build a prototype for our new project? Should we select the low-price contractor? Should we select the low-budget project?
For quantitative Risk Analysis, calculating the Expected Monetary Value (EMV) by using Decision Tree is an extensive technique. This article analyzes the decision tree analysis based on The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) while making critical decisions.
Expected Monetary Value (EMV) for Decision Tree Analysis
The decision tree analysis provides a template to calculate the values of outcomes and the possibilities of achieving them. It allows us to select the most suitable choice relying on the existing information and best forecasts.
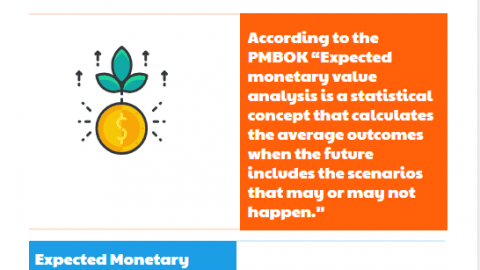
The PMBOK Guide defines The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) as a statistical concept that calculates the average outcomes when the future includes the scenarios that may happen or may not happen.
Probability x Impact is equal to The Expected Monetary Value (EMV). For the opportunities this value is positive and for the threats it is negative.
To learn how to calculate The The Expected Monetary Value (EMV), please read The The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) article.
Decision Tree Analysis Implementation Steps
Below are the decision tree analysis implementation steps :
1. List all the decisions and prepare a decision tree for a project management situation.
2. Assign the probability of occurrence for all the risks.
3. Assign the impact of a risk as a monetary value.
4. Calculate The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) for each decision path.
For better understanding, let’s make the Decision Tree Analysis by using an example.
Decision Tree Analysis Example
Suppose you are a project manager of a power plant project and there is a penalty in your contract with the main client for every day you deliver the project late. You need to decide which sub-contractor is appropriate for your projects critical path activities. But while selecting a sub-contractor, you should take into consideration the costs and delivery dates.
• Sub-contractor 1 bids $250,000. You estimate that there is a 30% possibility of completing 60 days late. As per your contract with the client, you must pay a delay penalty of $5,000 per calendar day for every day you deliver late.
• Sub-contractor 2 bids $320,000. You estimate that there is a 10% possibility of completing 20 days late. As per your contract with the client, you must pay a delay penalty of $5,000 per calendar day for every day you deliver late.
You need to determine which sub-contractor is appropriate for your projects critical path activities. Both sub-contractors promise successful delivery and high-quality work.
Basic Steps
Step 1: List decisions and prepare a decision tree for a project management situation.
In Figure 1 below, a decision tree is prepared based on the decisions, costs, and rewards of uncertain events.
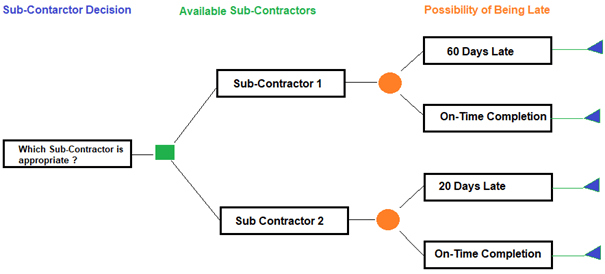
Figure 1: Decision Tree Analysis-Sub-Contractor Decision
Step 2: Assign the probability of occurrence for the risks.
In this example, the possibility of being late for Sub-contractor 1 is 30% and for Sub-contractor 2 is 10 %. This means that the possibility of completing on-time for Sub-contractor 1 is 70% and for Sub-contractor 2 is 90 %. In Figure 2 below the probability of occurrence for the risks are assigned.
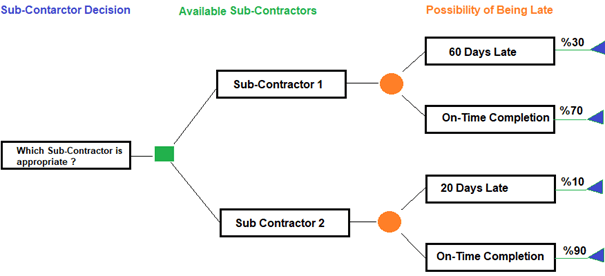
Figure 2: Decision Tree Analysis-Possibility of Being Late
Step 3: Assign the impact of a risk as a monetary value.
In Step 3 we are calculating the value of the project for each path, beginning on the left-hand side with the first decision and cumulating the values to the final branch tip on the right side as if each of the decisions was taken and each case occurred. Figure 3 below shows the value of each path.
Figure 3: Decision Tree Analysis-Sub-Contractor Decision
As shown in the figure, path values are calculated by the formulas given below.
Sub-Contractor 1
Path value of completing on-time = Bid Value = $ 250,000
Path value of being late = Bid Value + Penalty = $ 250,000 + 60 x $5,000 = $ 550,000
Sub-Contractor 2
Path value of completing on-time = Bid Value = $ 320,000
Path value of being late = Bid Value + Penalty = $ 320,000 + 20 x $5,000 = $ 420,000
Step 4: Calculate The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) for each decision path.
In Step 4, we are calculating the value of each node – including both possibility nodes and decision nodes. We begin with the path values at the far right-hand end of the tree and then proceeding from the right to the left calculate the value of each node. This calculation is called “folding back” the tree.
The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) of each node will be calculated by multiplying Probability and Impact. Figure 4 below shows The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) of each path.
As shown in the figure, The Expected Monetary Value (EMV) of each path is below.
Sub-Contractor 1
EMV = %30 x $ 550,000 + %70 x $ 250,000 = $ 340,000
Sub-Contractor 2
EMV = %10 x $ 420,000 + %90 x $ 320,000 = $ 330,000
In this simple example Expected Monetary Values (EMV) are very close. Now we are selecting Contractor 2 because of low cost and low possibility of being late.
Summary
In this article, we discuss the importance of decision tree analysis by the help of an example. Note that the decision tree analysis is a statistical concept which offers a powerful way of determining, finding out and analyzing uncertainty. It is an efficient tool that helps you to select the most suitable action between several alternatives. Also, this technique enables to present complex data for decision making visually. In order to perform a Decision Tree Analysis correctly, you need to know the Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Risk Analysis.
See Also

Francois Simosa is the head of training for the Gragados Training Associates, which provides special project management and risk management training programs.