Assumptions vs Constraints: Unraveling Key Differences in Project Risk Management
In our daily lives we often make assumptions for our decisions. However, constraints are the obstacles on the roads. If you are preparing for the PMP Certification exam, most probably you have thought about the examples of project constraints and assumptions. Many projects begin with limited accuracy. Only a few of them begin with adequate certainty. Some issues and facts are known at the beginning but most issues and parameters must be estimated during the planning phase. Successful project managers and business analysts keep in mind the effects of assumptions and constraints while managing their projects. In this article, we will review the key PMP concept: Assumptions vs Constraints and discuss common project constraints.
Table of Contents
Assumptions and Constraints
For better understanding let’s analyze the following real-life example;
Assume that you plan to go on a holiday and booked a flight. You planned to leave your home at 16:00 and reach the airport by 18:00. This is the assumption that you made for reaching the airport.
However everything does not happen as planned.
The most significant constraint is traffic density. It may prevent you to reach the airport on time. In a similar manner, projects have also assumptions and constraints that may effect the project objectives. Therefore, you need to identify and control these factors to complete your project successfully.
Assumptions Explanied
An assumption is something that is believed to be true based on our knowledge, experience, and information provided by our team members. These are anticipated events or issues that are expected to occur during our project life cycle.
Assumption analysis is a part of the risk management process. If it is not made properly analyze, it may affect the project’s health. The project management plans need to change if assumptions are verified wrong.
For example, you have assumed that all the consumables will be available during the welding activities. However, they were not available and you didn’t complete the welding activity.
After these examples for assumptions, let’s discuss constraints.
Constraints Explained
Assumptions and constraints have different meanings. Project constraints are anything that restricts or dictates the actions of the project team such as the limitation of cost, schedule, resources. Projects must be executed within the boundaries restricted by the constraints.
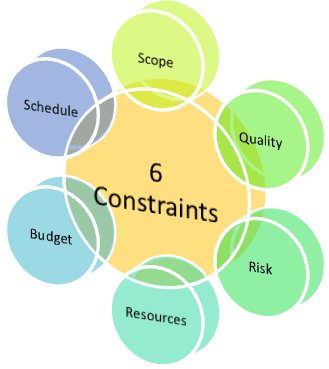
As per the PMBOK Guide, the following are the six constraints that are recognized as determining factors in project management:
• Scope
• Quality
• Schedule
• Budget
• Risk
• Resources
All of the six constraints influence each other in that anyone getting affected impacts one or more of the rest.
Unlike the assumptions, there are two types of constraints.
1. Business Constraints
2. Technical Constraints
Business Constraints
Business Constraints focus on the available time, money and resources for a project. Common business constraints include resource limitations and budget and time restrictions.
Technical Constraints
Technical constraints focus on architecture and engineering decisions that limit designs. For instance, we’re constructing an abutment, and according to the design, our abutment should be able to withstand a certain amount of pressure. This pressure limit is our technical constraint.
Summary
It is important to define, analyze and document project assumptions and constraints so that as the project progresses the project manager is able to verify and validate the accuracy of assumptions and capture lessons learned. Assumptions and Constraints are inputs to many project management processes. Note that Assumptions and Constraints are defined and documented in the project scope statement.
See Also
configuration management and change management
Contingency Plan vs Fallback Plan

Wanda is the Director of Blue Horizons Professional Training Services which focuses on the delivery of PMI-SP, Stakeholder Management and other project related workshops, training, mentoring and consulting services. She holds a Doctor of Project Management from Harward University.