Value Analysis & Value Engineering Methodology
Value analysis is a relatively new approach to managerial decision-making. It includes a set of techniques to identify unnecessary items or costs in a product or service in order to eliminate them without decreasing their quality and serviceability. It is a systematic approach that relies on the evaluation of techniques and tools in the various areas of concern by focusing on analyzing the ways of performance improvement so that the value of a product or service can be improved. Value analysis (also known as Value Engineering or Methodology) aims at achieving the maximum possible value for a given cost through a continuous process of planned actions. Now, let’s review the definition of Value Analysis (Value Engineering, Methodology) and talk about the techniques and advantages of it.
Table of Contents
Defining Value
Before discussing What is Value Analysis, let’s focus on the definition of value to provide a better understanding. Value is a subjective term that can be defined from different points of view. From a supplier’s perspective, value is directly related to the cost and function of a product while it may refer to various different meanings from a customer’s point of view. Because products and processes have multiple stakeholders that are related to multiple needs.
Collecting information is the starting point of value analysis. Before performing the value analysis, you should know the scope of the project, product, or service well. Then think about what the value is from each stakeholder’s perspective. Asking some questions will be helpful to determine their needs.
- What are the utilities or services to be provided by the product in order to achieve the objectives?
- Are there some specific factors to be considered?
The feedback received from the stakeholders will shape the design manufacturing processes of the end product.
The Formula of Value
Value is the consistent performance of functions to meet stakeholders’ needs at the lowest cost. It can be formulated by using the following formula;
- Value = Function/Cost
The function of the product defines what it is supposed to do or provide. Cost is the number of expenses to build up the product.
What is Value Analysis (VA)? Definition & Purpose
Project teams aim at improving projects, products and processes, and services by using systematic and structured methodologies. Value Analysis techniques (also known as Value Engineering or Methodology) are applicable to almost all industry projects or processes such as construction, business, IT, healthcare, administrative, etc.
Value Engineering was first applied in General Electric Co. during World War 2. Because, there were limited amounts of labor, material, and equipment resources to be used for manufacturing. After World War 2, Lawrence D. Miles developed this methodology in 1947. The methodology relies on two objectives;
- Improving the utility provided by the product
- Eliminating wastes
By focusing on the definition of value from the stakeholder’s perspectives, the steps or components of the production are classified as either value-added or non-value-added. This classification forms the reengineering of the design and production processes. The value analyst also considers replacing the components or elements with equivalent ones that are low cost. In conclusion, a substitution is made without reducing the quality of the product but reducing the production/material cost.
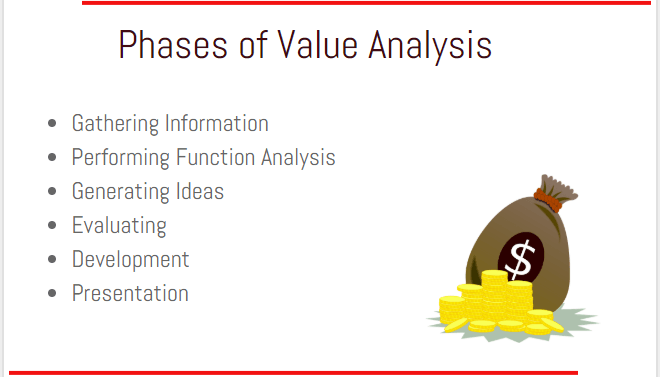
Phases of Value Analysis (VA)
Value Engineering Methodology is a systematic approach that can be considered as a problem-solving system that uses a set of specific tools, techniques, and skills. It assists all branches of an organization from engineering to marketing. While performing value analysis, you can use Pareto Chart, PERT Chart, and Gantt Diagrams, etc.
Value Analysis can be performed by following the six essential phrases.
Gathering Information
Gathering information includes identifying the requirements of stakeholder’s needs and accumulating information regarding the assumptions in order to understand the project/product better.
Performing Function Analysis
The next step is to determine the function of each element by breaking down the item into its sub-components. The purpose of this determination is to understand what contribution the element makes by focusing on the cost of each component. Then each function is classified as either primary or secondary to decide what will happen if each of them replaced from the process.
Generating Ideas
After generating information and classifying primary and secondary elements, the next step is to generate ideas on all the possible ways to achieve the required functions. Asking questions regarding the functionality of the product and brainstorming may be helpful to generate ideas. Investigating technology may give ideas regarding new materials or resources.
Evaluating
The evaluating phase includes gathering up the ideas and concepts in order to decide if they are feasible to follow.
Development
The development phase includes making a comparison between the design options in order to select the best alternative for improving the value. Elapsed time for production is a common unit of measure while making a comparison. Cost is another unit of measure for comparison. In addition to cost and time, handling, transportation, and other factors should be considered while selecting the best alternative.
Presentation
Presentation is the last phase in which you present the value recommendation to the stakeholders.
Advantages of Value Analysis
Value analysis techniques provide many advantages to organizations. Below are the main advantages of it.
- Improves the value of a product or a process.
- Helps to increase profits by reducing costs
- Helps to decrease the elapsed time for production
- Increases productivity
- Keeps team members aware of the latest trends and technology
- Promotes innovation and creativity
- Since it aims at the production of the most suitable product, customers become satisfied
- Helps to improve the functions of a process or a product.
Weaknesses of Value Analysis
Although the value analysis focuses on improving the value of a product or process by understanding its key components, it may lead to wrong decisions if it is not performed properly. Keep in mind the following notes for a successful application;
- Be free from prejudices and don’t make generalizations
- Be precise as much as possible
- Collect information from the best possible sources
- Calculate costs and determine the possible value to be realized.
Summary
Value analysis techniques are applicable to the design of products, services, and processes. The product or service under analysis should be capable of being divided into sub-elements. For example, in the case of product design, the product’s bill of materials provides essential information regarding the list and types of components. In the case of a production process, a task list provides the necessary information. Then the Value Engineer defines the value in the light of information that he gathered and analyzes the ways to add value by using this definition. Finally, the engineer proposes changes in design and production processes to eliminate, reduce, or replace elements that do not add value to the product.
Note that a process completed with VA is often more successful and efficient than a process without VA.
So, What do you think about the advantages of value analysis? Please share your experiences with us.
See Also
Further Reading
SAVE International Standard’s Body of Knowledge
Tim Cristini is a recognized thought-leader in Lean, Agile, Kanban, SAFe, Scrum, technical Agile practices, design patterns and emergent design. He is the CEO of NY FLEX Training









Protecting the value of our assets or even improving them for a better earning is significant.
we need to engineers everywhere ı think and Value Analysis & Value Engineering is not easy job
Value engineering is an organized attempt to optimize the overall value of the project in project management endeavors. Thanks 🙂