Unique Features of Spider Project
Part 1: Quantity Based Scheduling
1. Introduction
Spider Project is a powerful project management software developed in Russia and launched to the market in 1993. Since then its development has been ongoing and today it is the most functional and most popular project management tool in Russia, used in most large-scale programs with the customers in 36 countries. Spider Project was designed and developed based on project planning approaches, methods and requirements that existed in the USSR and still exist in today’s Russia. Therefore it has a lot of unique features absent in project management tools that are most popular in the West. Besides, in the USSR and Russia project modeling has been and is used not only for contract administration but also for optimizing the use of limited resources. Resource constrained schedule optimization has always been the primary goal of project management software development and implementation. I planned to write an article about unique features of Spider Project but just listing all of these takes too much space.
Table of Contents
So, in this article we will only discuss one of these features that I named Quantity Based Scheduling. Should the readers become interested in other differences between Spider Project and other tools, these will be discussed in further publications.
2. Activity Types
When people estimate activity duration, they consider the amount of work to be done that we call activity’s Volume and Productivity of the assigned resources. However, MS Project, Oracle Primavera and other popular tools do not feature such properties of project activities and resources. In Spider Project, activities have Volumes and it permits not only to calculate the duration of activity with known productivity of the assigned resources but also to apply different kinds of corporate norms such as unit costs and material requirements per volume unit for different activity types.
Spider Project has the following activity types:
- Duration (activity duration is an initial information)
- Productivity (activity volume is an initial information and duration is calculated after the productivity of the assigned resources becomes known)
- Milestones (zero duration activities that usually reflect the main events)
- Hammocks (activity duration and dates are defined by the external events)
- Switch (zero duration activity used for modeling conditional networks)
- Trigger (zero duration activity that happens with a certain probability and is used for modeling risk events)
Switch and Trigger type activities are used for modeling conditional and probabilistic branches in project networks and are employed in the Monte Carlo risk simulations.
Productivity, Switch and Trigger type activities exist in Spider Project only.
Volumes (amounts) of work to be done are usually set in physical units (meters, tons, miles, etc.) but they can also be set as expected resource hours or percentage. An activity is considered completed if the remaining volume is zero.
3. Project Resources
Project resources in Spider Project are divided into renewable resources (labor, machines) that are called Resources, and consumable resources that are called Materials. Resources and Materials are different objects, which permits Spider Project users to assign materials to resources: e.g. setting that a machine (resource) consumes a particular amount of gas or/and electricity (materials) per one hour of work.
Among other properties, renewable resources can have their own calendars.
Besides, Spider Project users can create resource crews as stable groups of resources that only work together. These crews are called multi-resources and, assigning multi-resources, project planners assign all resources belonging to these multi-resources. At any given moment, the composition of multi-resource may be changed (with some resources added, deleted, or replaced) in the multi-resources table and these changes will be automatically applied to all future assignments of this multi-resource. This feature is very useful for creating and analyzing multiple what-if scenarios.
Another option that is also useful: creating and assigning resource skills. Resources belong to the same skill if they can do the same type of works, replacing each other, although maybe with different productivity and cost. One resource can have multiple skills. When resource skills are assigned, Spider Project automatically selects who must do what based on the assigned resource availabilities, productivities and costs. This feature helps to optimize project schedules and resource usage.
5. Resource Assignments
Spider Project users can assign to activities individual resources, multi-resources or resource skills.
There are two types of resource assignments: team assignments and independent assignments.
Resources, multi-resources and skills belong to the same team if all assigned resources must work together and, if some of the assigned resources are not available, the whole team cannot work.
When resources can work independently of each other, they are assigned as different teams. An example: resources that work in different shifts on the same activity must be assigned in different teams.
When resources are assigned, project planner defines their required quantity, workload and productivity on this activity. Quantity is the number of specific resources; the workload is measured in percent and shows the percentage of its work time a resource must work on this activity; productivity is measured as an activity’s volume per work hour and must be defined for the driving resources or multi-resources.
When resources are assigned, activity duration is calculated as the ratio of activity volume and total productivity of assigned resources, which is modified by their workloads.
It is possible to set the ranges of assigned resource quantities and workloads. For instance, six workers were assigned to an activity with 100% workload but the minimal number of assigned workers is two and the minimal workload is 50%. With this assignment, two workers with 50% of their work time available can start working on this activity and other four can join in when at least 50% of their work time becomes available, using all available work time. In Spider Project, this type of assignments is called variable resource assignment and it helps to model the projects properly and optimize the use of project resources.
Spider Project plans and manages resource quantities and workloads. Other PM tools plan and manage resource hours only. It is not the same and ignoring resource quantities leads to erroneous resource constrained schedules and resource requirements reports.
A simple example of this problem: A Sample project consists of three parallel activities that require the same resource A with 60% workload. If only 2 units of resource A are available, then one of these three activities must be delayed because both of these 2 resources will only have 40% of their work time available instead of 60% required on the third activity (Exhibit 1). But when only the total resource hours (16 per day) are taken into account, all three activities can be performed in parallel, which is not true (Exhibit 2).
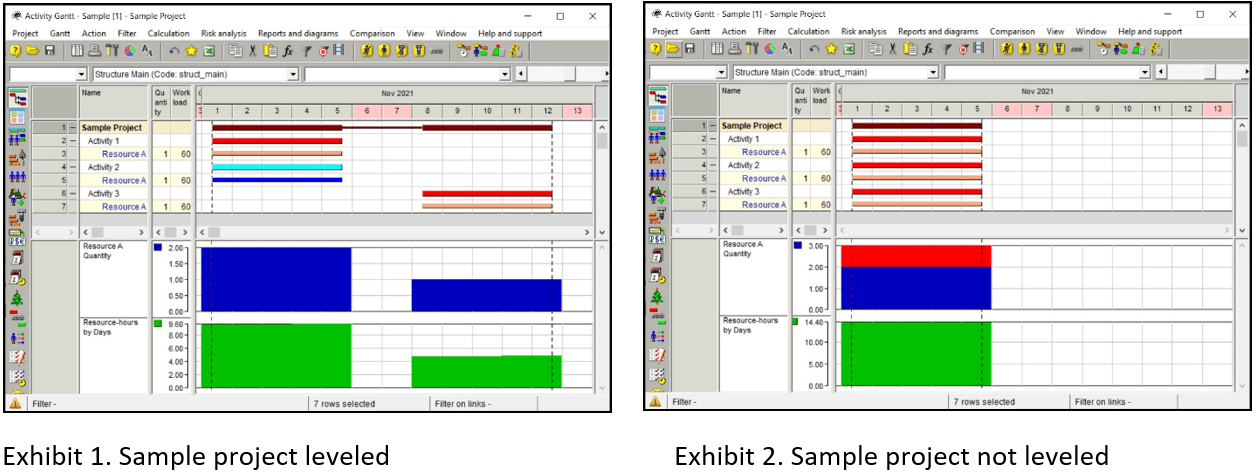
5. Material and Cost Assignments
Materials can be assigned to activities, resources and resource assignments.
Material consumption by renewable resources can be set as an amount per one hour of their work.
Activity and Resource assignment material requirements can be set as a fixed amount, amount per volume unit or per work hour.
Project cost consists of cost components. Spider Project users can define any number of direct and indirect costs like wages, cost of materials, cost of machines, taxes, overhead costs, etc., required for project cost analysis.
Spider Project features permits planning and managing parallel project budgets such as Expenses and Contract Cost, and enter multiple costs of the same activities, using any number of currencies.
Different groups of cost components can be included in cost centers. Thus, cost center Expenses can consist of wages, material costs, costs of machines and other cost components that represent the Contractor’s expenses, and cost center Contract Cost can consist of cost components defined by contract conditions.
Cost components can be assigned to Resources, Materials, Activities and Resource Assignments.
Resource cost is usually set as the cost of its work hour.
Material cost is set as the cost of material unit.
Costs can be also assigned directly to activities and resource assignments as fixed costs, costs per work hour and costs per volume units.
In most cases, material requirements are defined as the amounts per activity volume units; contractor expenses usually consist of assigned material and resource costs; and contract costs are defined as activity fixed costs and costs per activity volume units (unit costs).
6. Quantity Based Scheduling
Defining activity volumes, resource quantities and productivity, Spider Project plans and manages projects the same way people do it. Spider Project plans volumes of work in physical units and collects data on the actual amounts of work that has been done rather than mythical ‘percentages complete,’ which are hard to measure. Using Spider Project features, people assign and manage resource units instead of resource hours that lead to the wrong schedules and wrong information on project resource requirements.
When resource skills are assigned, activity duration is determined during project scheduling when the program selects which resources with the required skills but with different productivity will be assigned.
Another application of activity volumes are the volume lags of activity dependencies. For example, it is possible to define that a succeeding activity may only start after a certain volume of work is completed on the preceding activity. Time lags are less reliable because, for some reasons, completing the required volumes can take more or less time than expected.
As has been mentioned earlier, introducing activity volumes permits to create and use the corporate norms.
Spider Project users can define and assign activity types. Activities are of the same type if they have the same properties such as unit costs, material requirements per volume unit, required resource crews, and assigned resource productivity.
It is possible to create and manage the databases of the corporate norms that in Spider Project are called Reference books. These reference books usually contain the data common for the same type activities. The companies that use Spider Project as their corporate project and portfolio management tool usually create their internal corporate reference books and use them for project scheduling and budgeting.
With corporate reference books, it is sufficient to enter activity type and its volume of work and everything else (activity cost, resource assignments, resource productivity and workloads, material requirements) will be obtained automatically by just applying the corporate reference books.
With reference books project planning becomes much easier, more reliable because initial information is based on the corporate standards, and more flexible because changing some data in a corporate reference book allows changing the respective data in all projects that are linked to this reference book. For example, some data can be simply redefined in the reference book and the changes will automatically apply to all projects that use it.
In Spider Project it is possible to define activity, resource and dependency lag calendars, which are used in a different way from other tools. While other tools use activity or resource calendars, depending on activity type, in Spider Project the working time must be such in both activity and resource calendars.
To try quantity based scheduling, please download Spider Project Demo from here to explore its features.
Spider Project Team partners in Australia recently started to create and publish video tutorials in English that can be useful for learning Spider Project.
Let us know if you are interested in the following articles describing other unique features of Spider Project.

PMP, GPSF, GCMF, Founder of Moscow, Russia PMI® Chapter
General Manager of Spider Project Team – the leading Russian project management consulting company with branches an partners in Russia, Brazil, Colombia, Kazakhstan, Romania, and Ukraine.
Spider Project Team developed Spider Project, most powerful professional Project Management software package that is now used in 36 countries.
An author of 4 books and more than 150 papers on Project Management.
Speaker at many PMI® and IPMA Congresses and Conferences since 1994.
Involved in management of many large scale projects including the development of Russian Pacific Area, preparation for 2014 Winter Olympic Games, construction of all stadiums for 2018 FIFA World Cup, etc.
Has an experience of managing projects in many application areas including aerospace, construction, mining, manufacturing, oil&gas, shipbuilding, software development, telecommunications.









I have used CMMS (such as SAP or Maximo). I think there are duplicate areas (ie similarities) between CMMS and Spider Project. So, what is the best integration between them? Is it application integration or data integration?
Thank you,
English tutorials about spider project are very scarse in youtube.
is there any updated userguide available for downlaod so that one can try provide some tutorials on youtube based on the user guide ?
Hi Josh, we already discussed this in LinkedIn.
Hi Tarik. Spider Project tutorials made vy our Australian partners can be found here https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCHT9_PtvWQOizAcezSsj52g
Marcus Possi from Brazil published books on Spider Project https://www.spiderproject.com/index.php/books
You may be interested in discussions on Spider Project at planningplanet.com where special forum was created https://www.planningplanet.com/forums/spider-project
Updated User Guide exists in Russian https://www.spiderproject.com/ru/images/img/manual/SP_user_manual.pdf
It consists of 961 pages and was not translated into English yet. We plan to do it.
I will be glad to answer your questions on Spider Project here or at planningplanet.com forum. You can also ask questions in LinkedIn.