Decoding Project Finances: Understanding Cost Classification – Direct Costs vs. Indirect Costs
Cost classification is an important process in budgeting, accounting, and project management. Cost classification and categorization of expenses help project teams to understand what kind of costs will be spent during the life cycle of their project. For example, in a construction project, a cost control engineer lists the direct cost and indirect cost items while creating the baseline budget. Basically, Direct costs vs indirect costs is an important concept that every project manager should know. Although there are some significant differences between them, it is not easy to make a clear distinction between direct and indirect costs all the time. A distinction can be made depending on the nature of the product and business.
Table of Contents
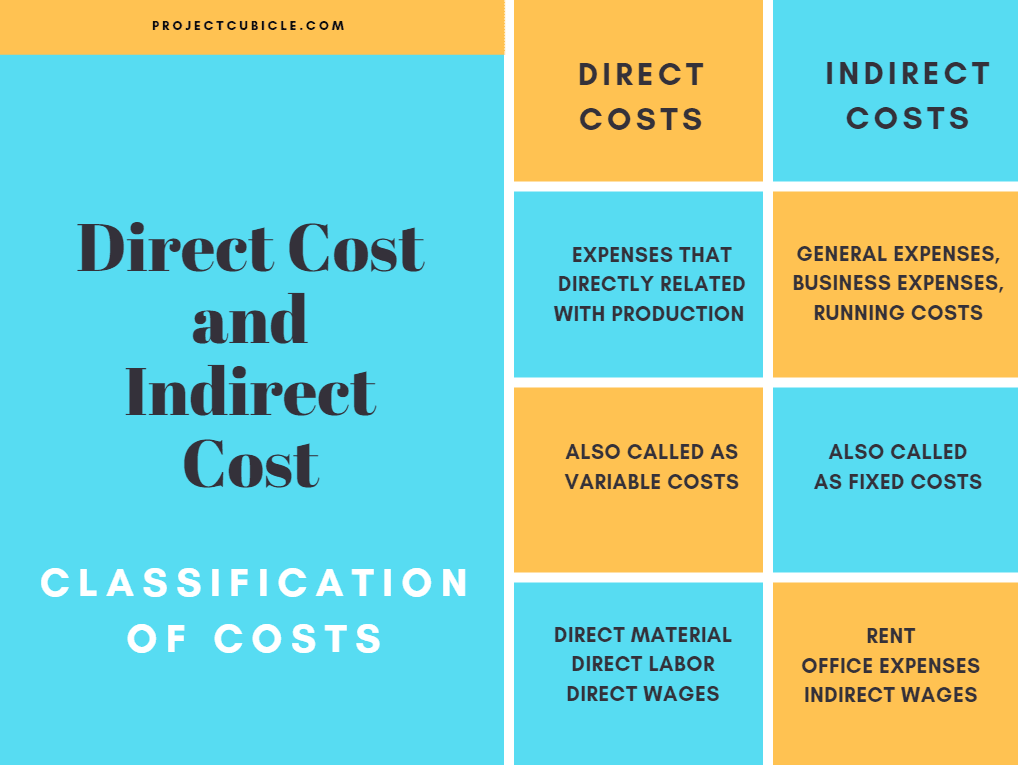
Typically, direct costs are attributable to a product, goods, or service itself. In other words, direct costs are directly related to production. On the other hand, indirect costs are those which is required to produce the product but not directly related to the product itself. This article answers the following typical question: what are the primary differences between direct and indirect costs?
What is the Importance of Cost Classification for Project Budgeting?
Cost classification is the process of distinguishing costs into subcategories. For this purpose, a classification method is required to categorize and prioritize costs for financial modeling. Many different types of cost classifications can be made such as;
- Direct and Indirect Costs
- Fixed and Variable Costs
- Customer Costs
- Departmental Costs
- Manufacturing Costs
If you don’t understand the difference between the cost categories, you will have difficulties while managing a project’s budget or operating a business.
Therefore, it is important to recognize the classification while purchasing material or estimating project expenses.
Assume that you are a project manager of a house construction project and the client makes a change request related to changing the perimeter walls from reinforced concrete to masonry. The first thing you should do is to make a unit price analysis and classify the costs according to their type. Material, labor, and machinery costs are direct costs and increases as the amount of work increases.
On the other hand, project management and operational costs are indirect costs that don’t directly relate to the amount of work but increase as the duration of the project increases.
Basically, costs can be divided into two major categories according to the element/nature. For better understanding, let’s analyze each concept.
Direct Cost

A direct cost is a price that can be utterly attributed to the production of products or services. Some costs, such as direct materials, direct labor, equipment are examples of common direct costs.
In some cases, it is possible to classify an indirect cost as a direct cost. For instance, the salary of the manager who controls multiple concrete batch plants would be considered as an indirect cost for each batch plant. However, that manager’s salary would be a direct cost for the department which comprising all of those concrete batch plants.
Direct costs are often variable costs. If the manufactured units increase, direct costs increase. Because creating more units requires more materials and resources.
An Example for Direct Costs
Assume that, you will produce 1000 m3 concrete in the batch plant. You need 300 tons of cement to produce 1000 m3 concrete and 1 ton cement costs 100 $. So you need 30,000 $ to purchase cement. This is your direct cost. As the quantity increases direct cost increase.
Indirect Cost

Indirect costs are those which affect the whole company such as depreciation, accounting services, general supplies, board salaries, and overhead costs. They are not spent just on only one product. Overhead costs, ongoing costs, project management costs, operational costs are indirect costs.
Indirect costs are often fixed costs. But also they can be variable.
For instance, the rental cost of your head office is a fixed cost. The quantity of manufactured units doesn’t affect your rental price. Another example of a variable cost is your heating and cooling expenses that can change on a monthly basis.
For cost controlling purposes, many companies try to limit their indirect costs as a proportion of direct costs.
An Example for Indirect Costs
Going back to the same batch plant example. Assume that this month you will produce 1000 m3 concrete. If you increase the production and produce 1500 m3 concrete this does not change your head office costs or marketing costs.
More Examples for Direct Costs and Indirect Costs
Direct Cost Examples

The following are a few examples of direct costs
- Laborer’s wages
- Wood, Glass, Cement, Concrete, Rebar, etc.
- Handles, locks, hinges
- Direct materials
- Consumable supplies
- Freight in and out
- Sales commissions
- Royalty Payment
- Patent Holder
- Consultants
- Tools
Indirect Cost Examples
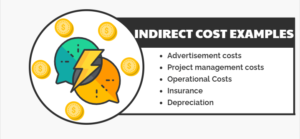
The following are a few examples of indirect costs.
- Advertisement costs
- Project management costs
- Operational Costs
- Insurance
- Depreciation
- Manager’s salary
- Indirect costs related to transport
- Administration cost
- Indirect employee’s salaries
- Security cost
- Office cost
- Selling & distribution cost
- Factory overheads
What are the Primary Differences Between Direct and Indirect Costs?
Below are some differences between direct costs and indirect costs.
- It is easy to determine direct costs considering the product or service. On the other hand, it is not easy to identify indirect costs. Detailed analysis is required to identify indirect costs.
- Direct costs are attributable to a specific product, department, goods, or service. On the other hand, indirect costs are attributable to multiple products or services.
- Direct costs are variable costs that change based on the quantity of a product or service. However indirect costs are fixed costs.
Difficulties in Cost Classification
There are some costs that can not be classified easily either direct or indirect. Some indirect costs such as hiring a consultant or traveling expenses are sometimes categorized as direct costs depending on the circumstances. In that case, organizations often classify them according to their nature and usage.
Overhead costs are indirect costs that are related to direct costs.
Summary
If you want to classify cost according to the element or nature, you should use two categories which are direct and indirect costs. Cost classification process is very important in project cost management. It enables to develop an effective cost control and profit planning system. If you don’t know which cost is direct which expense is indirect, you cannot perform cost control effectively. Also, it is helpful for decision making.
It is significant to have a clear understanding of cost classification. During the procurement of goods or a service, you can compare their direct and indirect costs to your project separately. One option may involve more indirect costs than the other. So you can select the alternative with the low indirect cost.
Classification of expenses has an important impact on federal tax payments. It also affects a company’s cash flow and financial health.
Note that direct costs vs indirect costs is a very important concept for claiming tax deductions.
See Also
Project Status Report Template

Vice President, İntelligent Design & Consultancy Ltd
Over 12 years of global & rich experience in Portfolio & Program Delivery Management in leading & managing IT Governance, PMO, IT Portfolio/Program, IT Products, IT service delivery management, Budget Management, and more.





This is a great post! I have been trying to get my head around the different cost types and how to classify them for my next project. Thanks for the help!