Industry 4.0 Trends and Smart Factories
Modern industrial developments have continued for several hundred years, and three major industrial revolutions have emerged until today. Currently, we are in the fourth industrial revolution as Industry 4.0 trends and smart factories. In the first industrial revolution (1.0), industry was turning water to steam power. The second industrial revolution (2.0) occurred 30 years later when the first mass-production assembly line working by electricity was functional. In the late 1960s, the first programmable logistic controller (PLC) allowed factory automation via the use of electrical and IT systems, marking the beginning of the third industrial revolution (3.0).
Table of Contents
Industry 4.0 refers to the simultaneous maturation of many important technological advancements that may drastically alter the manufacturing industry’s environment. As these technologies — advanced robots, artificial intelligence, sophisticated sensors, cloud computing, and big data analytics – connect with one another, the real and virtual worlds will merge and revolutionize the industrial business.
It takes over production with robots that communicate with each other, detect the environment with sensors, and realize the needs by analyzing data and aims to produce better quality, cheaper, faster, and less wasteful production. In addition, it monitors physical processes with cyber-physical systems in modular smart factories, allowing objects to communicate with each other and people, and as a result, decentralized collaborative decisions are made.
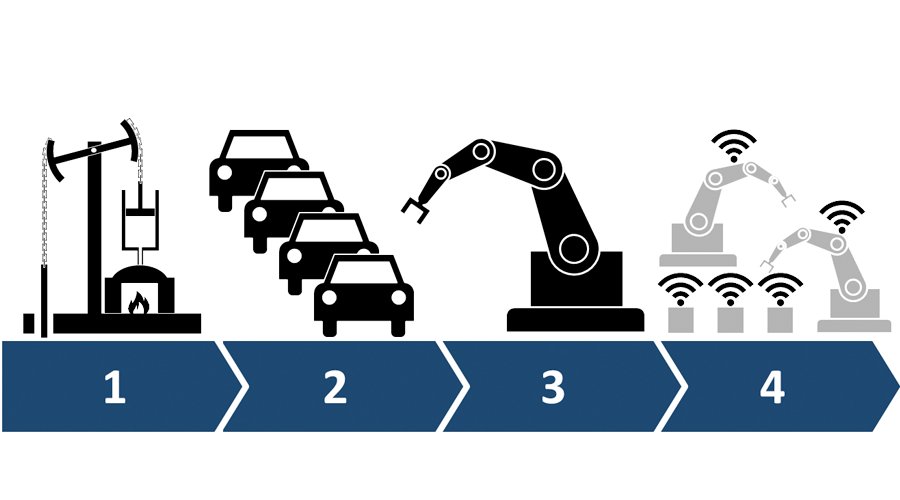
From the first industrial revolution to the fourth industrial revolution and Industry 4.0 trends:
The world continues to develop with four revolutions in industry.And we know that in the transitions between these revolutions, innovations have taken their place along with previous technologies. The important milestones that emerged in the four industrial revolutions of the world, namely Industry 1.0 to 4.0, are explained below.
- Application of Mechanical Production Facilities
- Transition to Mass Production Based on Electricity and Division of Labor
- Automation of Production Processes
- Autonomous Machines and Virtual Environments
The elements that started in 2000 are the triggers and infrastructure of Industry 4.0. In other words, they are the components of today’s smart factories. Thus, companies now needed interdisciplinary work and the fourth industrial revolution. So that all objects communicate and interact over the internet, has emerged. Smart factories are the non-digital component of Industry 4.0 and are concretely visible and observable parts of society.
Potentials of Industry 4.0 and Trends:
Objectives of Industry 4.0 are to provide mass customization of products produced by information technologies, to ensure automatic and flexible adaptation of the production chain, to monitor parts and products, to facilitate communication between parts, products, and machines, to implement human-machine interaction (HMI) paradigms, to optimize production with the internet of things in smart factories, and in terms of value, it can be listed as offering new types of services and business models. Despite the growing complexity of the Industry 4.0 system, it also has the potential outlined below.
- Increasing competition and flexibility arising from the dynamic nature of business processes (quality, time, risk, robustness, price, and environmental friendliness),
- Eliminating malfunctions in the demand chain,
- Optimizing decision making with real-time end-to-end visibility
- Provide increased resource productivity(it produces the highest output from a given volume of resources). And efficiency (uses the lowest possible amount of resources to achieve a given output),
- Creating value opportunities (innovative services, new forms of employment, development opportunities for SMEs and start-ups),
- Reducing energy and personal costs.
Industry 4.0 Trends :
Industry 4.0 encompasses numerous technologies and associated paradigms. Some of these emerging paradigms are Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Enterprise Resource Planning, Internet of Things ( IoT ), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), 3D printing, Cyber-Physical Systems, cloud-based manufacturing, smart factory, smart product, big data, etc. These features are not only highly correlated with internet technologies and advanced algorithms. But also indicate that it is a value-added information processing and industrial value-added process.
In Industry 4.0, one of the important places where objects communicate with each other is the smart factories. They are equipped with intelligent technologies and are also called dark factories because there are no people to work with. The number of workers in China’s first dark factory. And it produces mobile phone modules, decreased by 90%, while the rate of defective product formation dropped from 25% to 5%.
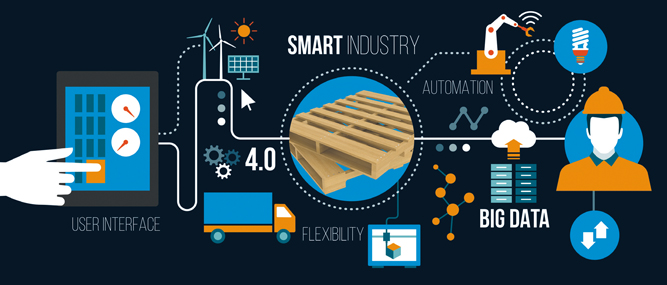
The impact of smart factories on this revolution:
Among the factors that triggered this revolution, and at the very center of the revolution that created the transformation in the manufacturing industry, are smart technologies and smart factories. This revolution, of course, affects and changes all service sectors and infrastructures, along with manufacturing. Smart Factories of Industry 4.0 and trends include smart machines and systems that detect business needs with sensors, communicate with other remote production tools via the internet. Then extract the production information they need from Big Data in cloud systems. The communication and interaction of the means of production with each other are provided via the internet.
All production resources (sensors, actuators, machines, robots, conveyors, etc.) do not only automatically exchange information, but also be conscious and smart enough to predict and maintain machines to control the production process and manage the factory system. In addition, many production processes such as product design, production planning, production engineering, production, and services can work modularly.
Summary
Industry 4.0 trends currently has a significant impact on the manufacturing industry and this impact will continue exponentially in the future. And many smart factories working with minimal people have already started production. It will enable us to achieve unprecedented levels of operational efficiency. And also allow us to accelerate our productivity by introducing new types of advanced manufacturing and industrial processes toward machine-human collaboration and symbiotic product realization in the future. In other words, the new level with digital transformation and Industry 4.0 will ensure that people, objects, and systems come with interconnection. Therefore, companies that want to increase their competitiveness in the future should apply this revolution to their production organizations. So that they should apply technologies such as smart robots, cyber-physical systems, and cloud-based manufacturing in their factories.

Simon Bonghez is currently a Director and Project Management Consultant with LIFESPEED India, and a Project Management Consultant & Speaker.










