Kanban Methodology for Project Management
Kanban methodology is a project and process management tool developed by an industrial engineer Taiichi Ohno in the late 1940s. In the beginning, it is introduced as an integral part of the lean manufacturing production system. The purpose of the Kanban approach was to increase the productivity of the Toyota Production System by eliminating wastes without causing a decrease in productivity. The Japanese word kanban (看板) means visual (kan) card (ban). Kanban laminated cards are used in the Toyota plants to guide lean production by communicating demands. These cards specify the tasks that need to be done just in time. In this article, we will talk about the Kanban boards and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of Kanban Methodology.
Table of Contents
Main Principles of the Kanban Methodology
In the 1940s, Toyota Production System adopted “just in time” manufacturing which relies on the pull system. Unlike the push approach, the amoınt of production depends on the customer demand. Toyota Production System has been arranged according to the lean principles in order to create more value.
As discussed above, the word “Kanban” means signal card which refers to the time to pull the next item through the production line. In project management, Kanban is a methodology of organizing work and workflow by increasing visualization with Kanban cards.
The keystone of Kanban cards is to reduce the amount of work in progress. It eliminates wastes generating from complexity and context switching and encourages collaboration to improve the system.
Kanban methodology aims at an efficient change management system and customer and stakeholder satisfaction. It is an alternative agile technique.
Below are the basic principles of Kanban
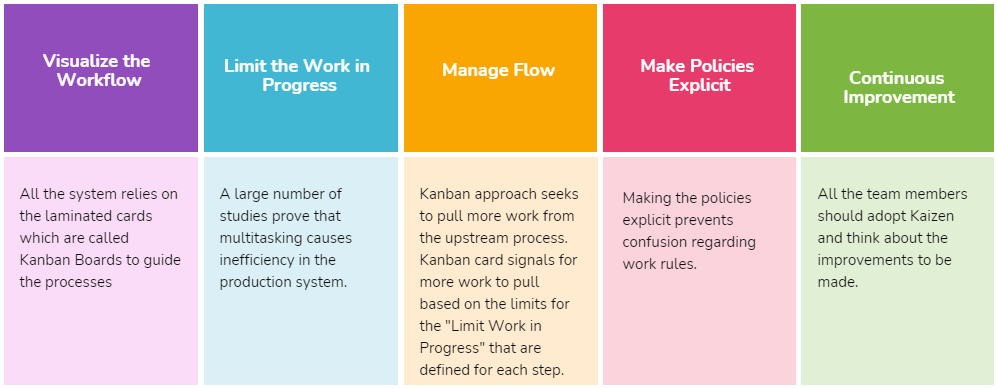
- Visualize the Workflow
- Limit the Work in Progress
- Manage Flow
- Make Policies Explicit
- Continuous Improvement
Let’s discuss each principle in detail.
Visualize the Workflow with Kanban Boards
All the system relies on the laminated cards which are called Kanban Boards to guide the processes. Simply put, the Kanban board is a tool to visualize the workflow and optimize it by promoting the participation of the team. Digital boards can be used as well as physical boards for visualizing and optimizing the workflow.
In the Kanban Boards, work items and tasks move from left to right and each step represents the situation of the task.
Basically, a Kanban Board has three steps;
– To Do
– In Progress
– Done
Additional steps such as In Development, In testing, Planned can be added to the Kanban board based on the requirements. Unlike Scrum boards, Kanban boards may involve many teams and even the whole organization.
In software development projects, visual mapping is the first step of a Kanban approach. The team creates a value stream map as a Kanban Board to manage the processes.
Limit the Work in Progress
A large number of studies prove that multitasking causes inefficiency in the production system. For example, if a programmer was working on two code writing tasks that should take four hours each, due to the multitasking, the total completion duration may be more than eight hours. Kanban methodology limits the number of tasks to be done at each step to prevent the inefficiency caused by multi-tasking.
Manage Flow
Kanban approach seeks to pull more work from the upstream process. Kanban card signals for more work to pull based on the limits for the “Limit Work in Progress” that are defined for each step.
Make Policies Explicit
All the process Kanban Methodology should be based on policies. Some of the policies are under the control of the project team, other policies are ordered by the management. Making the policies explicit prevents confusion regarding work rules.
Continuous Improvement
Kanban methodology aims to maintain continuous improvement within the production system. It is every team member’s business to improve the system by sharing thoughts. All the team members should adopt Kaizen and think about the improvements to be made.
Just like other project management methodologies, Kanban has some advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of the Kanban Methodology
No matter which industry they are operating in, adopting Kanban makes organizations more agile. Because visualizing every task on a whiteboard is an effective method to keep the team members on the same page.
Kanban methodology provides many advantages to the production system of an organization. Below are some of the most important ones.
- Promotes transparency in project management
- Improves teamwork
- Promotes Agile workflow
- Promotes participation of the team
- Reduces waste
- Increases productivity
- Increases customer satisfaction
- Allows flexibility
- Helps to minimize the amount of inventory
Disadvantages of the Kanban Methodology
Below are the disadvantages of the Kanban Methodology;
- It requires a dynamic environment.
- It requires an effective real-time communication system.
- Kanban board must be viewed by the team constantly
- Necessary actions should be taken quickly for the Kanban cards. Because outdated cards cause defects and problems.
- Cards and categories may cause complexity.
- It is not applicable to all industries and projects.
Summary
Kanban is an effective tool for project management. Considering other forms of Agile, Kanban provides a more viable approach. Although Kanban was first applied to the Toyota Production System, it became popular for other industry projects such as software development. Kanban is an alternative Agile technique that is associated with Lean practices. Therefore organizations which are familiar with Lean are more open to Kanban. Kanban methodology enhances performance by decreasing the number of tasks and wastes that do not add value to the product. Necessary actions are taken simultaneously while performing many tasks at the same time.
Kanban is a common framework used to implement agile software development. Real-time communication and transparency plan important roles in this methodology.
In the past, laminated cards and whiteboards were widely used to activate the processes. Today a great number of software and internet-based tools are available for the use of Kanban. These tools are capable of defining each process step, creating work items, and moving them across the board as the work progresses.
In this article, we discuss Kanban Methodology and the key aspects of it. Are you using Kanban in your production system? If you have anything to add or share regarding Kanban, you can use the comments section below.
See Also
Agile Project Management Methodology
Scrum Master Interview Questions
External Reference

Over 20 years in portfolio management, streamlining business processes, and systems integration. Utilizing best practices: PMI, Scrum, Agile, Kanban, Lean/Six Sigma, CMMI, ITIL and MOF. Extensive experience in managing in cross functional environment, getting to the root of the problem, bringing stakeholders together to resolve them. Vice President at Force3M Training.









Thanks a lot for a very useful article. I have found everything that I needed to know about Kanban here. I already heard it is a very efficient tool that makes life much easier 🙂 But never tried. There are many useful tips here as well: kanbantool.com 🙂