Prototyping in Software Development and Why it’s Important
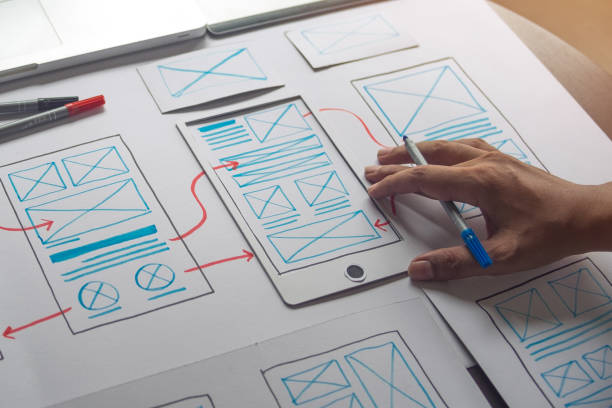
A prototype is essentially an initial model of a product, made to test the components of the original idea. Prototyping in software development before going ahead with the real-world product, or putting the idea into mass production, is a way of testing the original concept and understanding where changes or improvements might need to be made. Many products are products of a prototype, from video games to cars and even futuristic robots.
Table of Contents
In software development, a prototype can be created to suit a specific need. Whether that’s to test one aspect of a digital development or an entire app. Prototypes in this sense can consist of basic level blueprints right through to more advanced, fully interactive, coded products, depending on the requirements.
Why is software prototyping important?
There are many reasons why it’s vital to create a prototype, particularly in this current climate where technology is increasing at speed and the UK government is looking towards a digitally innovative future:
Save time and money
Digital development often comes with high costs and features can take months to create. By making an initial prototype, a developer can identify features that might need more work or those which fail to meet user needs. This way, there’ll be minimal wasted time and effort on the real product.
Visualisation
Often, to be able to engage with a product, you need to be able to see it in its working state. A prototype does exactly that and can even foster a more creative process from the developers who might spot something they otherwise wouldn’t have thought of.
Feedback
A key aspect of prototyping in software development is user feedback. Whatever product is being developed, the user experience is the most important element. Trialling an app with potential customers is one of the best ways to ensure the software fits user needs. Feedback should be collected and reported back to developers to enable a smooth final creation process.

The different possible prototypes
There are a few different techniques when it comes to software prototyping:
Rapid
This is where a design model becomes ready quickly, with the intention to discard it after testing, or only use a section of it in the real product. It’s often used at the initial stages and there can be multiple rapid prototypes for different aspects of the same product. PCB prototypes are commonly used across rapid techniques, depending on the software requirements, as they provide a fairly cheap and efficient way of testing various functions.
Evolutionary
This is where the prototype adapts and evolves alongside the design. It usually consists of at least some basic coding and lets the user engage and interact, enabling feedback on user experience. Rather than throwing this model away, it often evolves into the real, final product, due to its expansion and continually added functions.
Incremental
This involves looking at each part, or function, individually and giving every section its own prototyping in software development. The end goal here is to put each module together to create the final product.
Whichever technique is used, it usually results in an improved, final software product.
Software Prototyping in a Variety of Ways
Depending on your needs, you could create a software prototype by going through the several steps given below. Or you might merely focus on one phase to communicate your ideas.
-
Handmade Drawings and Paper Wireframes:
Regardless of how basic the drawing or wireframe may be, it may be good to first sketch your notion on paper. It is also a functional prototype.
When making a paper prototype, it is not necessary with artistry since the goal is not to generate a final and polished design. Instead, it may represent a significant step towards the realization of an abstract idea. You must go to the real concrete in order to complete the hand drawing stage.
-
Wireframes
The wireframes are the basic 2D diagrams of a software program, commonly referred to as low-fidelity designs for prototyping in software development. They are an upgrade over paper designs of software program interfaces, which are just straightforward line drawings. They often represent an early concept for the product and are the work of a team in charge of its development and design. Digital wireframe production is similar to sketching up product plans. With the exception that less style, color, and visual. They are produc of using of specialist software programs, like Invision, Sketch, Adobe, and Figma, among others.
Wireframes have the ability to be turned into clickable prototypes. They are interactive groups of linked visual panels that may mimic the functionality of a genuine application. The main contrast, though, is that no actual coding has been done. You will now have a decent concept of how the application will look and work in its final form. But it will still be easy to make any required changes.
Why Should You Start a Product’s Development with a Software Prototype?
Here are a few explanations for why prototyping in software development before beginning programming a software project makes sense.
It is crucial to test, validate, and iterate design ideas early on.
It doesn’t matter whether you have an exact vision in your brain of how your program should look when it’s done. Iterating on a prototype allows you to get at the ideal product design as quickly and efficiently as you can. At each step, you will have the option to include user feedback. It is allowing you to be sure that your time and resources are for the right features.
Consider building a prototype of your concept in order to convince possible funders or early adopters. This will enable you to explain or illustrate your proposal to prospective supporters more precisely.
It is not only economical. But also a low-risk enterprise to create a prototype of your idea to see whether there is any interest in it.
Prototypes have the advantage of being customizable to your needs and available in a range of complexity levels. With a lot of ideas, are you still in the beginning phases of brainstorming? Use paper drawings, which can be ready without spending any money. Are you ready to get feedback from prospective consumers on a challenging product? Create a clickable prototype that exemplifies and brings to life your idea.

Ananya Prisha is an enterprise level Agile coach working out of Hyderabad (India) and also founder of High Level PM Consultancy. Her goal has been to keep on learning and at the same time give back to the community that has given her so much.