Risk Management: What Is Cyber Insurance? How to Manage Cyber Risks?
Explore the world of cyber insurance and learn how to effectively manage cyber risks. Understand the importance of risk management in cyber security, its benefits, and steps to mitigate cyber threats.
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s digital age, where technology drives businesses and transactions, the risk of cyber threats and attacks is ever-present. Cybersecurity breaches can lead to significant financial losses, data breaches, and damage to a company’s reputation. This is where cyber insurance and effective risk management come into play. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of cyber insurance, understanding what it is, its significance, and how to efficiently manage cyber risks to safeguard your business and digital assets.
Risk Management: What Is Cyber Insurance?
Cyber insurance, often referred to as cyber liability insurance or cyber risk insurance, is a specialized type of insurance designed to protect individuals and businesses from the financial impact of cyber-related incidents. These incidents can range from data breaches and hacking attacks to identity theft and system disruptions. Cyber insurance provides coverage for the costs associated with responding to and recovering from these incidents.
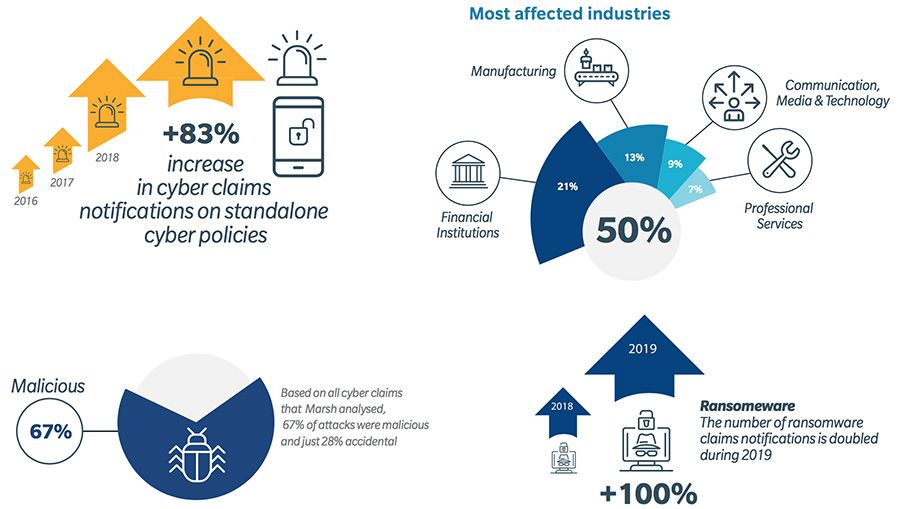
The number of claims on cyber insurance policies rising steeply
Coverage Areas of Cyber Insurance:
- Data Breach Costs: This includes expenses related to investigating the breach, notifying affected parties, and providing credit monitoring services for affected individuals.
- Business Interruption: Coverage for financial losses resulting from a cyber incident that disrupts business operations, leading to loss of revenue.
- Ransomware Attacks: Some policies cover ransom payments and expenses associated with recovering data after a ransomware attack.
- Legal and Regulatory Costs: Coverage for legal fees and penalties resulting from regulatory investigations or lawsuits due to a cyber incident.
- Public Relations and Crisis Management: Expenses related to managing the public relations fallout after a cyber incident to restore a company’s reputation.
- Cyber Extortion: Coverage for situations where cybercriminals demand payment to prevent a threatened attack.
- Third-party Liability: Protection against claims from third parties, such as customers or partners, who may have been impacted by a cyber incident involving your organization.
Managing Cyber Risks:
- Risk Assessment: Identify and assess potential cyber risks specific to your organization, considering the types of data you handle and your technological infrastructure.
- Security Measures: Implement robust cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, regular software updates, and employee training in cybersecurity best practices.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive plan outlining steps to take in the event of a cyber incident. This should include protocols for containment, communication, and recovery.
- Regular Testing: Conduct frequent cybersecurity assessments, vulnerability testing, and simulated cyberattack drills to identify weaknesses in your defenses.
- Employee Training: Train your employees to recognize phishing attempts, practice secure password management, and understand their role in maintaining cyber hygiene.
- Data Backup: Regularly backup critical data and systems. In case of a ransomware attack or data loss, having backups can expedite recovery.
- Vendor Management: If you rely on third-party vendors, ensure they also follow robust cybersecurity practices to prevent supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Cyber Insurance: Consider purchasing cyber insurance tailored to your organization’s needs to provide financial protection in case of a cyber incident.
- Compliance: Stay updated with relevant data protection and privacy regulations and ensure your organization is in compliance.
- Continuous Improvement: Cyber threats evolve, so regularly review and update your cybersecurity strategy to adapt to new risks and technologies.
Importance of Cyber Insurance
Cyber insurance is crucial for several reasons:
- Financial Protection: Cyberattacks can result in substantial financial losses due to data recovery expenses, legal liabilities, and business interruption. Also, cyber insurance helps mitigate these financial risks.
- Data Breach Costs: Handling a data breach involves notifying affected parties, providing credit monitoring, and dealing with legal consequences. Also, cyber insurance assists in covering these expenses.
- Reputation Management: A data breach can severely damage a company’s reputation. Also, cyber insurance often includes provisions for public relations efforts to restore a company’s image.
Benefits of Cyber Insurance
Investing in cyber insurance offers numerous benefits:
- Cost Savings: Without insurance, a cyber incident’s costs can be crippling. Cyber insurance ensures that the financial burden is significantly reduced.
- Customized Policies: Cyber insurance policies can be tailored to an organization’s specific needs, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Legal Assistance: Insurance providers often offer legal resources to handle legal aspects following a cyber incident.
How to Manage Cyber Risks
Effectively managing cyber risks involves a multi-faceted approach that includes preventive measures, incident response plans, and strategic risk mitigation strategies.
Risk Assessment and Prevention
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Regularly assess your organization’s digital infrastructure for vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit.
- Employee Training: Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as identifying phishing emails and using strong passwords.
- Firewalls and Antivirus: Implement robust firewalls and up-to-date antivirus software to protect against external threats.
Incident Response Planning
- Designate a Team: Form a dedicated team responsible for handling cyber incidents promptly and efficiently.
- Communication Plan: Create a communication plan that outlines how to inform stakeholders, employees, and customers in case of a breach.
- Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up critical data and have a solid recovery plan to minimize downtime.
Cyber Risk Mitigation
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data to make it unreadable in case of a breach.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Implement multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to user accounts.
- Regular Updates: Keep software, applications, and systems updated to patch vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
FAQs
Q: Is cyber insurance necessary for small businesses?
A: Yes, cyber insurance is essential for businesses of all sizes, as cyber threats can impact any organization regardless of its scale.
Q: Can cyber insurance prevent cyberattacks?
A: Cyber insurance doesn’t prevent attacks, but it provides financial protection and resources for recovery.
Q: What does cyber insurance typically cover?
A: Cyber insurance can cover data breach costs, legal fees, public relations efforts, and even business interruption losses.
Q: How much cyber insurance coverage do I need?
A: The coverage amount depends on factors like the size of your organization, the nature of your data, and potential risks.
Q: Are there exclusions in cyber insurance policies?
A: Yes, policies may exclude certain types of attacks or situations, so it’s important to review the policy details thoroughly.
Q: How often should I update my cybersecurity measures?
A: Regular updates are crucial. Cyber threats evolve quickly, and outdated measures can leave you vulnerable.
Conclusion
In a digital landscape fraught with cyber security and risk management, understanding cyber insurance and effective risk management in cyber security strategies is paramount. Cyber insurance provides the safety net needed to navigate the aftermath of a cyber incident, while proactive risk management in cyber security measures significantly reduces the likelihood of such incidents. By implementing preventive measures, planning for incident response, and embracing cyber insurance, you can safeguard your business, customer data, and reputation in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats.
Hello, I’m Cansu, a professional dedicated to creating Excel tutorials, specifically catering to the needs of B2B professionals. With a passion for data analysis and a deep understanding of Microsoft Excel, I have built a reputation for providing comprehensive and user-friendly tutorials that empower businesses to harness the full potential of this powerful software.
I have always been fascinated by the intricate world of numbers and the ability of Excel to transform raw data into meaningful insights. Throughout my career, I have honed my data manipulation, visualization, and automation skills, enabling me to streamline complex processes and drive efficiency in various industries.
As a B2B specialist, I recognize the unique challenges that professionals face when managing and analyzing large volumes of data. With this understanding, I create tutorials tailored to businesses’ specific needs, offering practical solutions to enhance productivity, improve decision-making, and optimize workflows.
My tutorials cover various topics, including advanced formulas and functions, data modeling, pivot tables, macros, and data visualization techniques. I strive to explain complex concepts in a clear and accessible manner, ensuring that even those with limited Excel experience can grasp the concepts and apply them effectively in their work.
In addition to my tutorial work, I actively engage with the Excel community through workshops, webinars, and online forums. I believe in the power of knowledge sharing and collaborative learning, and I am committed to helping professionals unlock their full potential by mastering Excel.
With a strong track record of success and a growing community of satisfied learners, I continue to expand my repertoire of Excel tutorials, keeping up with the latest advancements and features in the software. I aim to empower businesses with the skills and tools they need to thrive in today’s data-driven world.
Suppose you are a B2B professional looking to enhance your Excel skills or a business seeking to improve data management practices. In that case, I invite you to join me on this journey of exploration and mastery. Let’s unlock the true potential of Excel together!
https://www.linkedin.com/in/cansuaydinim/










Hi thank you for posting this article on Risk Management. It’s really helpful looking forward for articles like that.