Contingency Plan vs Fallback Plan
Here we will talk about the topic; Contingency Plan vs Fallback Plan with examples. Contingency plan and fallback plan are common risk management terms. If you are working in the field of risk management, most probably you know when and how to use them. Of course, they are created to manage identified risks within a project. However, if you are new to risk management, you might be doubtful about which plan is suitable for the situation.
Table of Contents
Basically, risks can be classified into many categories such as identified risks, unidentified risks, primary risks, secondary risks, positive risks, negative risks, etc. In order to manage the risks of your project, you can use two kinds of reserves which are management and contingency reserve.
But what about the plans? Which plan is suitable for managing what type of risks?
In this article, we will give quick answers to these questions.
Let’s start with the definitions.
Identified Risks
Risk identification is the process of identifying negative and positive risks that have impacts on the project.
Identified risks (also named as known risks) are those which can be identified and analyzed before they occur. Risk response strategies can be established to manage the identified risks proactively. Contingency Reserves are added to the project budget to manage the identified risks.
Unidentified Risks
Unidentified risks, also named unknown risks are those which can not be identified and analyzed before they occur. Unidentified risks cannot be managed proactively. In order to deal with them, Management Reserves are added to the project budget to manage the unidentified risks.
Contingency Plan and Fallback Plan
Both plans are developed during the Plan Risk Responses process to deal with identified risks (known unknowns). They are complementary to each other. Let’s go deeper and discuss the major differences between them.
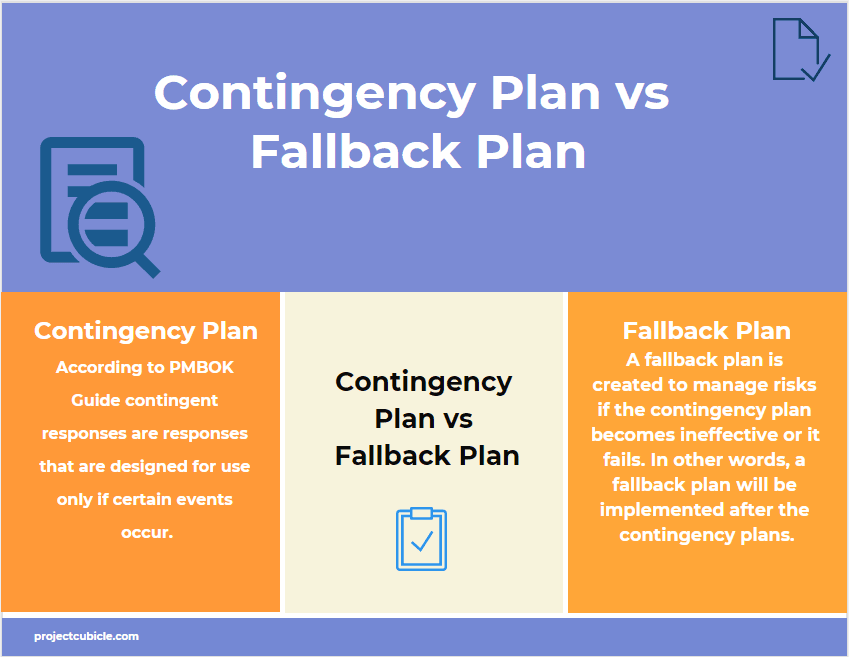
Contingency Plan

The term contingency can be defined as an event that may occur but is not certain to occur.
According to the PMBOK Guide contingent responses are responses that are designed for use only if certain events occur.
Based on this definition, a contingency plan is a part of the project management plan that will be implemented if an identified risk occurs. A contingency plan can be thinkable as “Plan A”.
Simply put this plan is a plan that will be implemented if a threat or an opportunity occurs. It describes specific actions that must be taken.
Contingency Plan Example
Assume that you are a project manager of a school construction project. The site crews are performing plastering works. The weather may be cold in the next 5 days. Therefore, you make a plan that says if the weather is cold, all the windows will be covered with a plastic cover in order to prevent the plastered walls from freezing. This is the contingency plan for this risk event.
A second example of the contingency plan is as follows. Assume that you are a warehouse chief and you received auto spare parts which are lying out in the open site.
According to your plans, “If there is a possibility of rainfall, all the auto spare parts will be covered with waterproof cloth.” This is your contingency plan in case of rain.
Fallback Plan

A fallback plan is created to manage risks if the contingency plan becomes ineffective or it fails. In other words, a fallback plan will be implemented after the contingency plans. It can be considered as a backup plan for the contingency plan which is generally made to manage residual risks.
A fallback plan can be thinkable as “Plan B”.
Fallback Plan Example
Considering the same school construction example, suppose that the weather becomes colder than forecasted.
Therefore, you will implement the fallback plan because the contingency plan becomes ineffective. The fallback says that if the weather becomes colder than forecasted, heaters will be used in order to prevent the plastered walls from freezing.
For the second example, you are the warehouse chief and the auto spare parts are lying out in the open site. The rain continued for a long time which is longer than expected.
Therefore, you will implement the fallback plan because the contingency plan becomes failed. The fallback says that if the rain continues for a long time, you will bring an excavator to dig ditches in order to prevent the auto spare parts from the flood.
Contingency Plan vs Fallback Plan – Keystones
- Contingency plans and fallback plans are complementary to each other. Once the contingency plan becomes inactive, you will implement the fallback plan.
- Both Contingency plans and fallback plans are used to manage identified risks within a project.
- A contingency reserve must be added to the project budget in order to manage the contingency and fallback plans.
Summary
Risks may occur in any type of project, and the objective of project risk management is to protect the project against the destructive effects of risks. The risk management process helps to identify, assess, avoid, transfer, minimize, accept and share risks. Potential project risks and their characteristics vary from one project to another. Project risks may be either identified or unidentified. Both plans are designed to manage identified risks on a project.
There are several methods used for responding and managing risks in project management. One of these methods is to prepare a contingency and fallback plan. Both of them are created during the Plan Risk Responses process. The contingency plan should be implemented when an identified risk occurs. However, if the contingency plan fails, the fallback plan should be implemented to manage the identified risk.
In this article, we discuss risk management terms. We hope that it will be useful for the attendants who will take the PMP Certification exam. If you want to add something or share your experiences, you can use the comment box below.
External References

Francois Simosa is the head of training for the Gragados Training Associates, which provides special project management and risk management training programs.